Mouse
Mus musculus
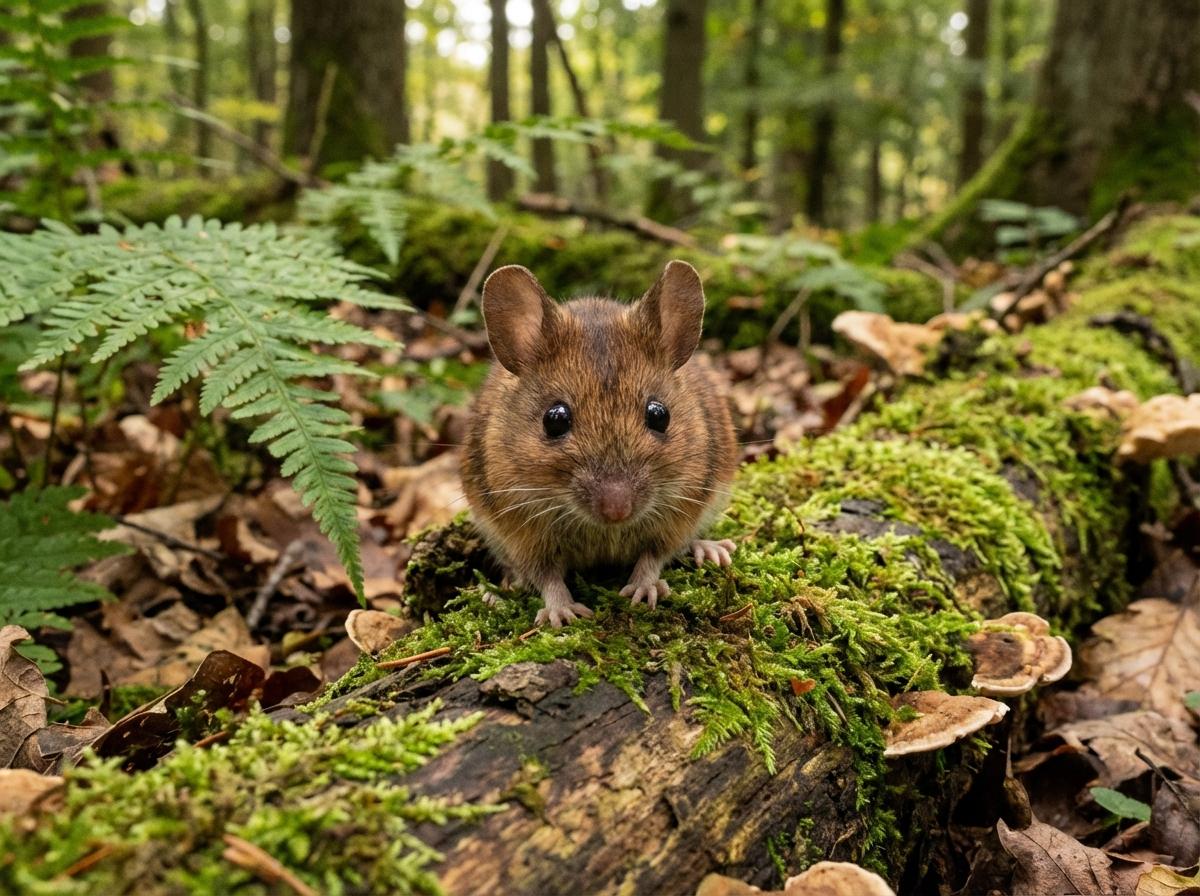
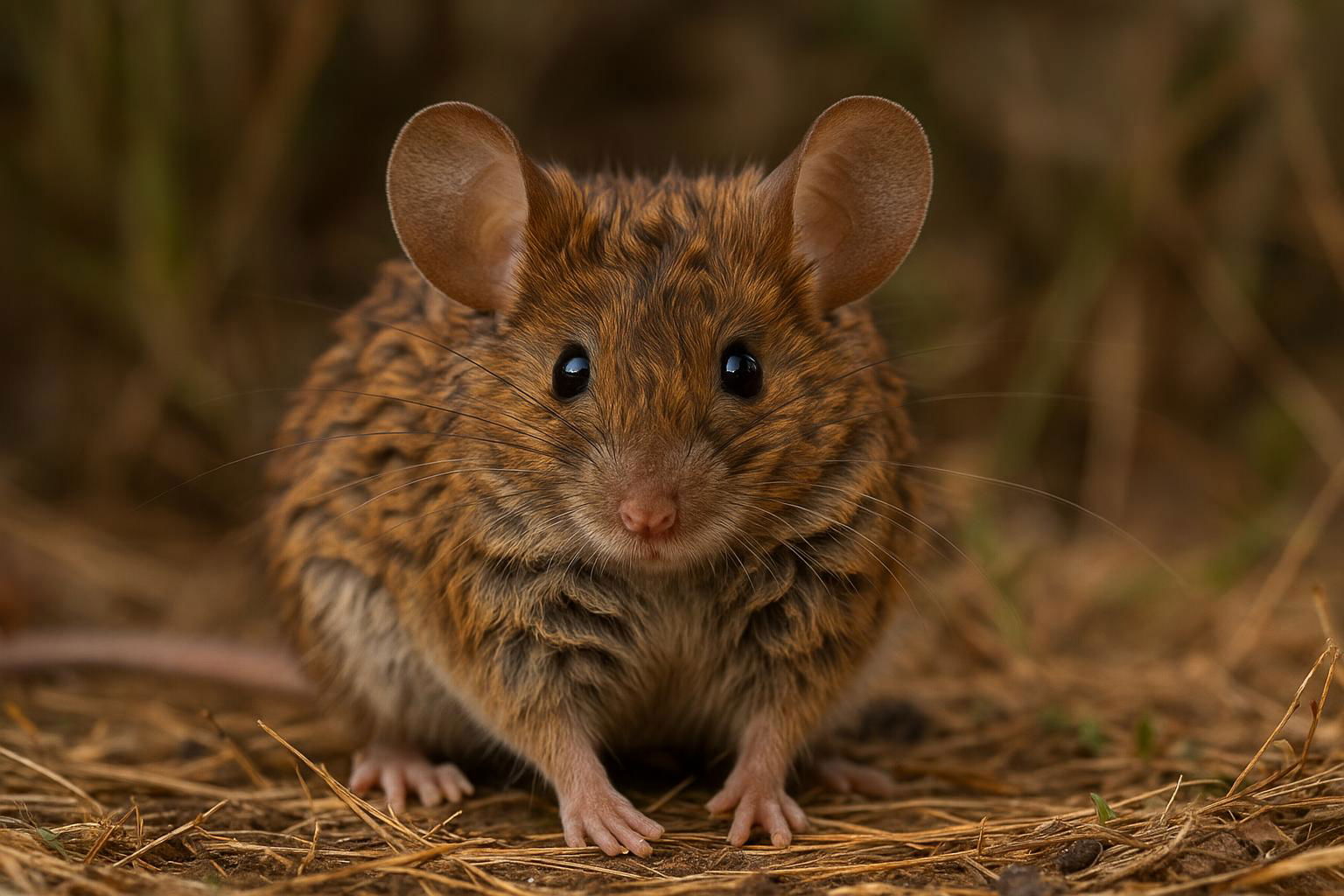
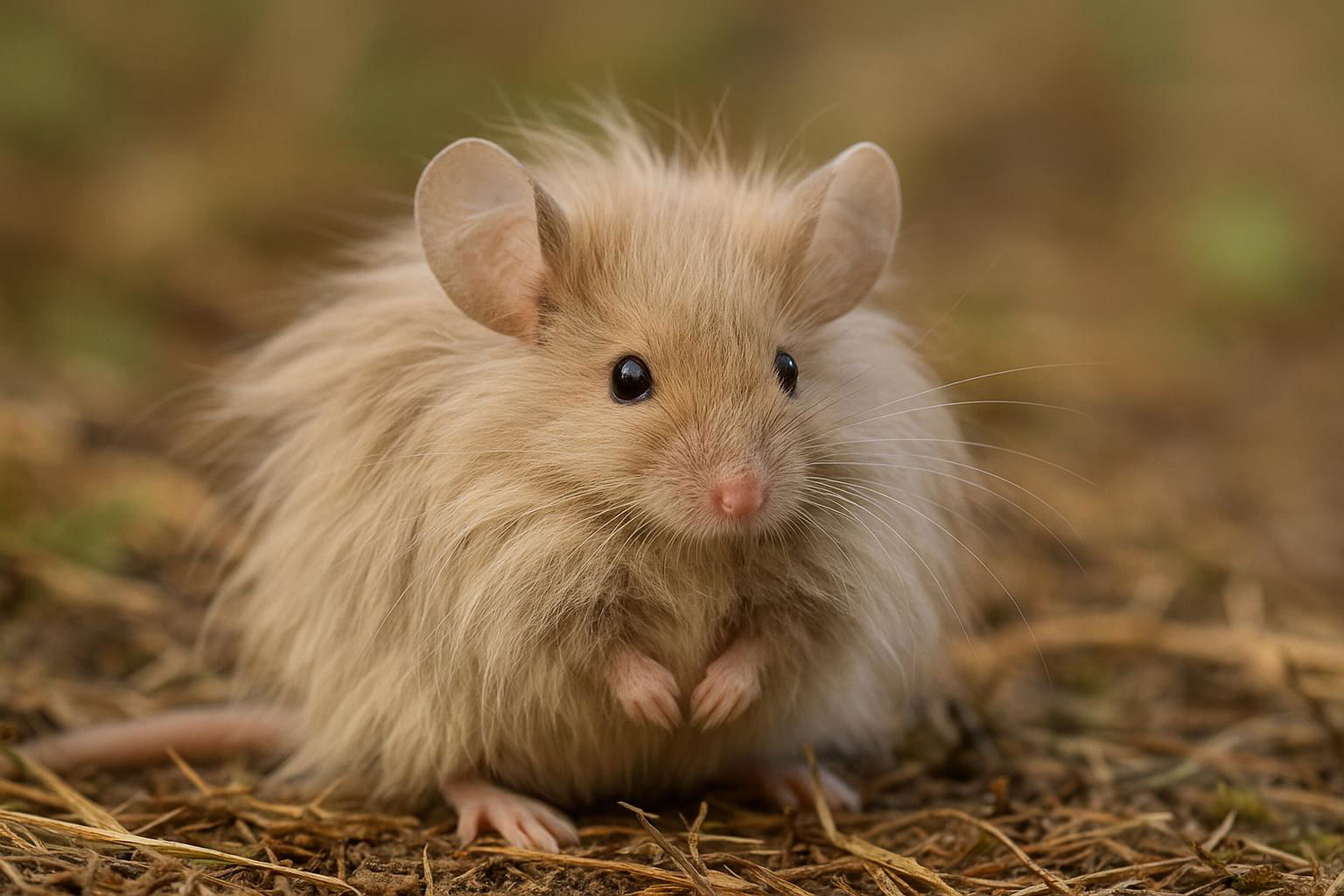
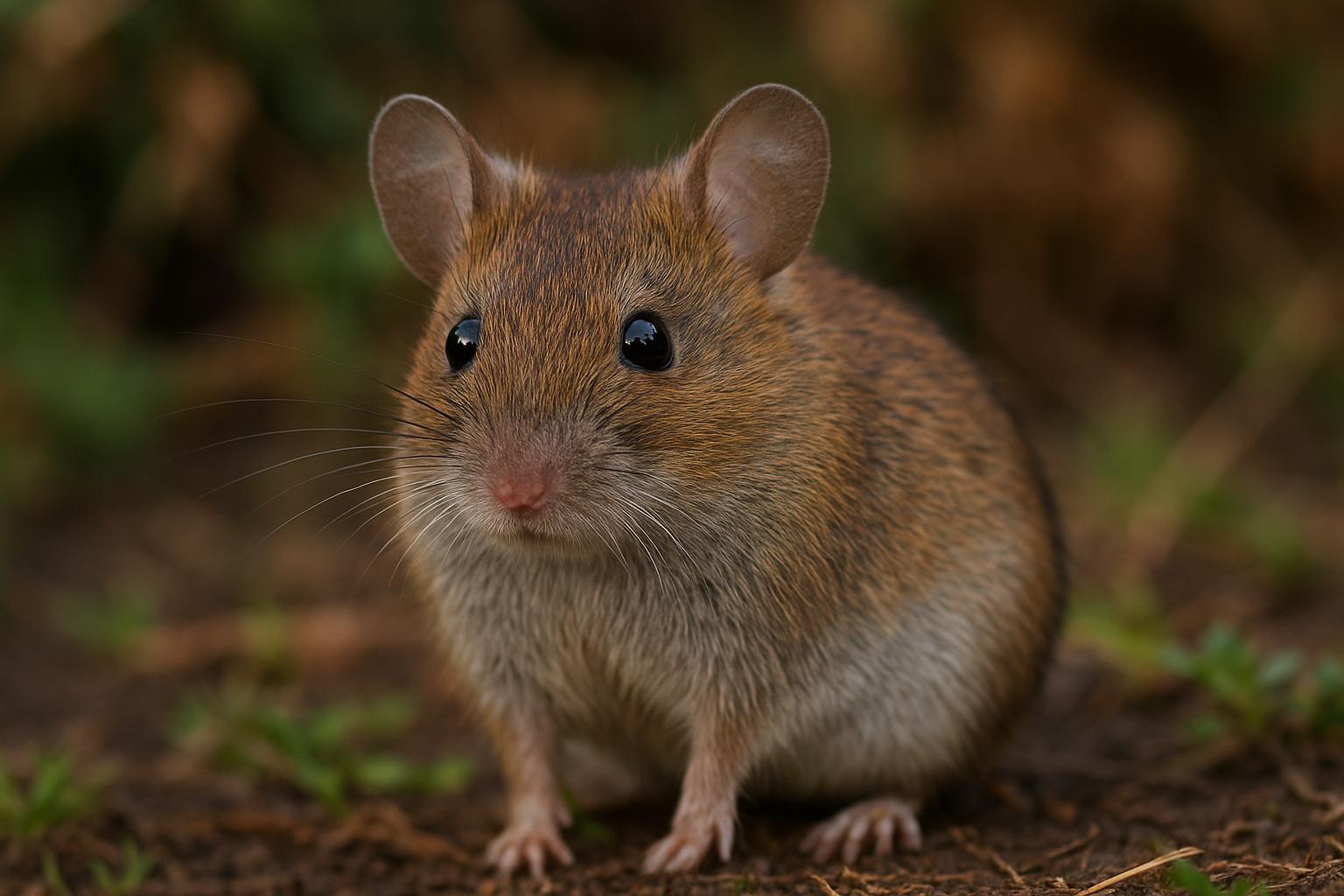
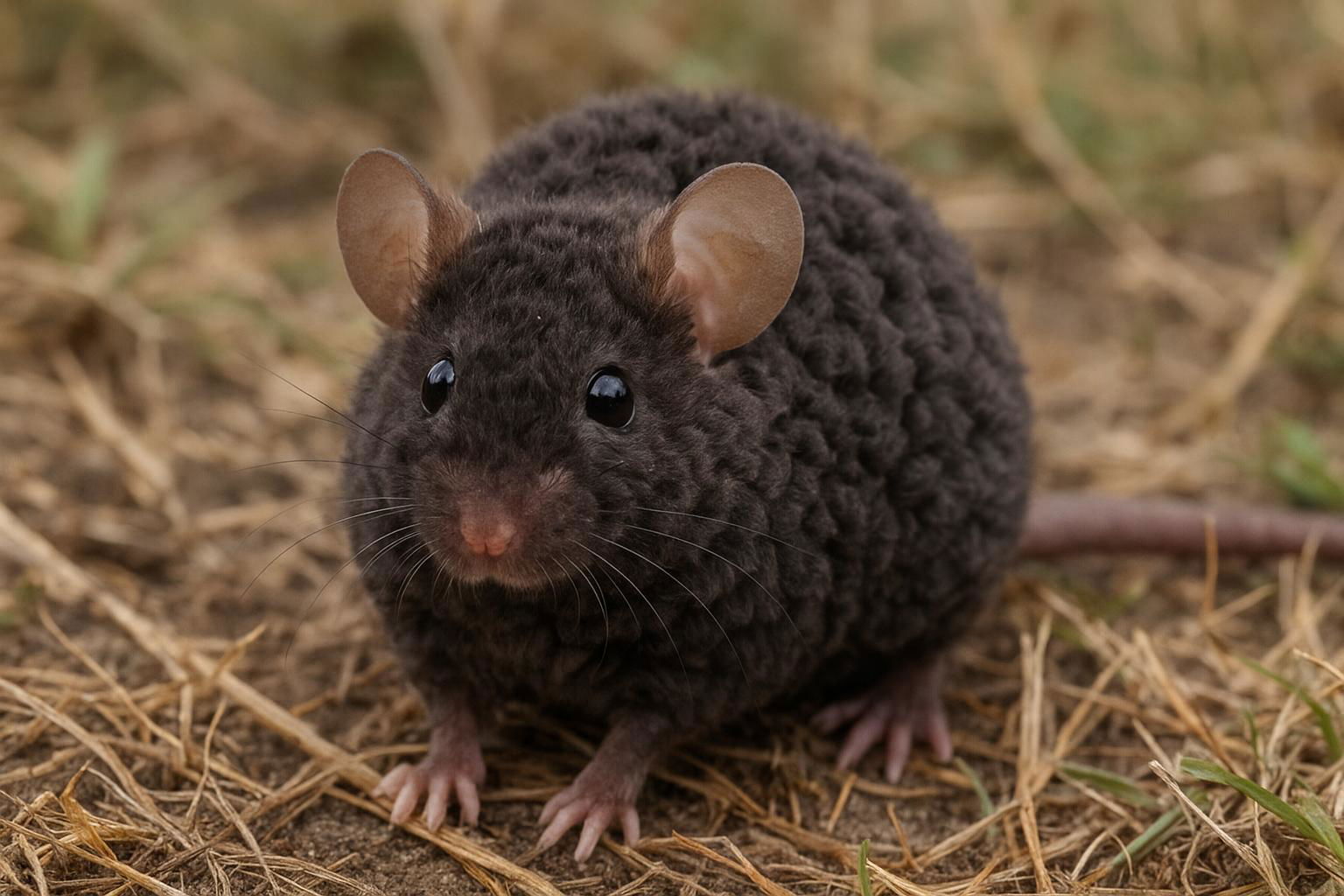
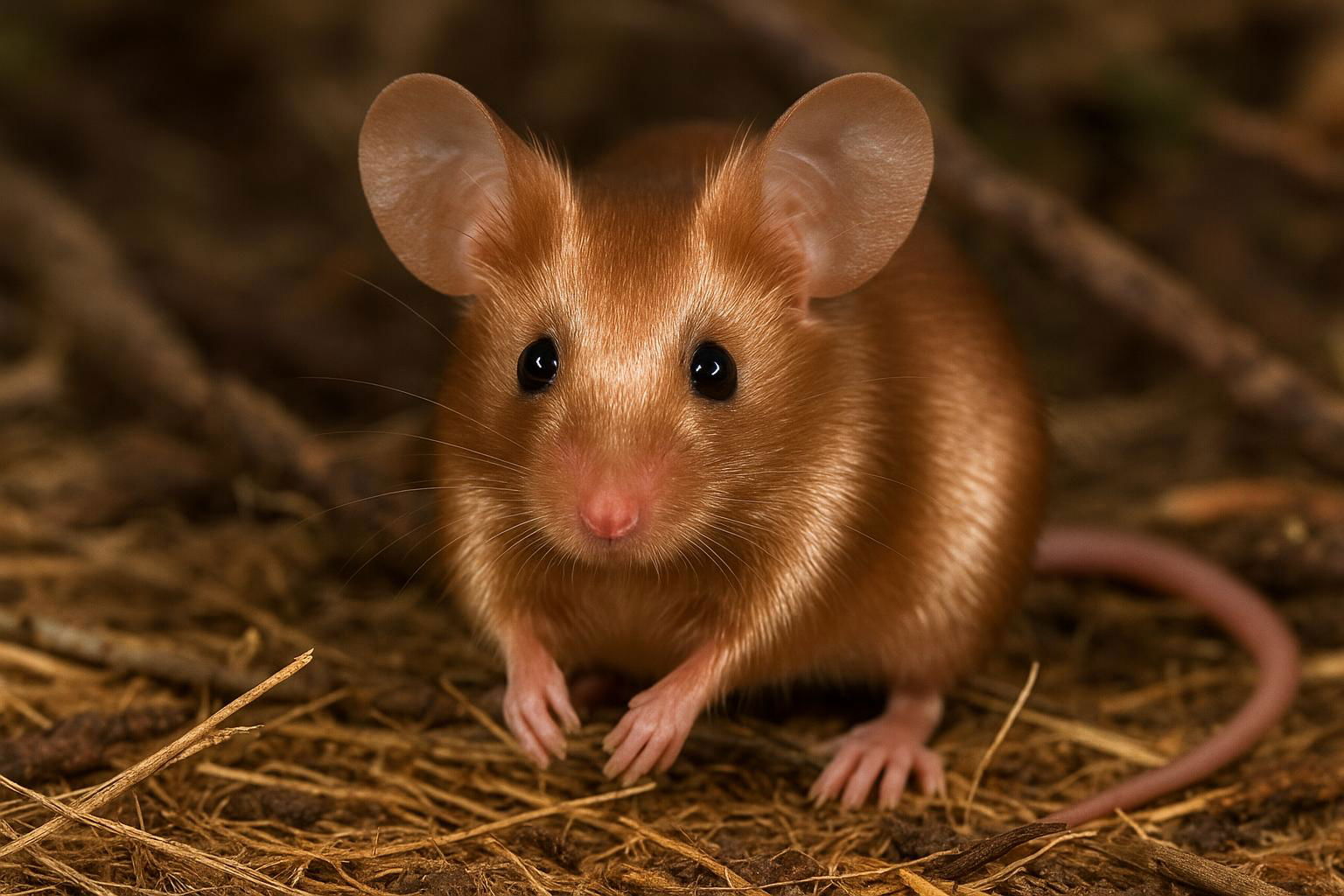
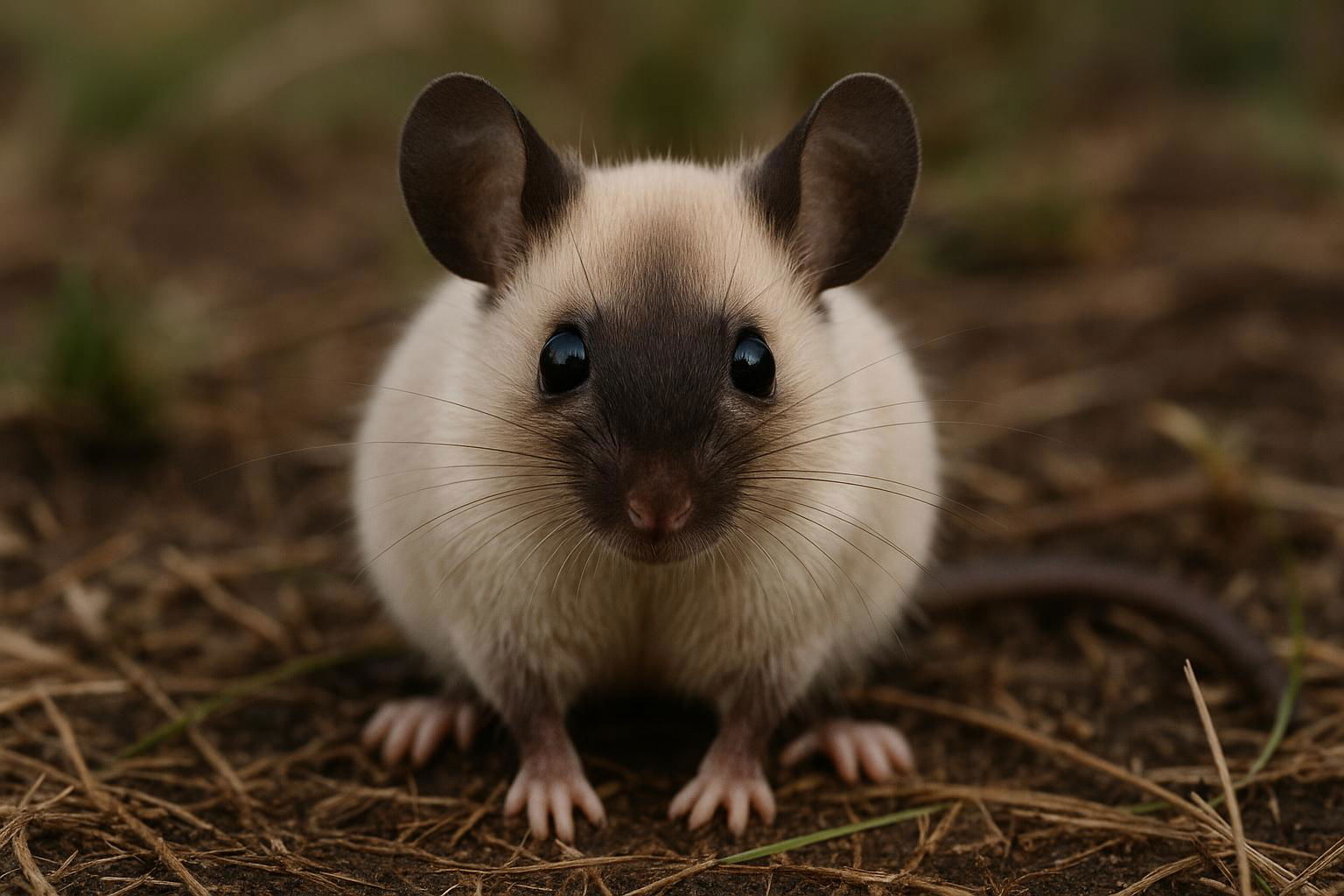
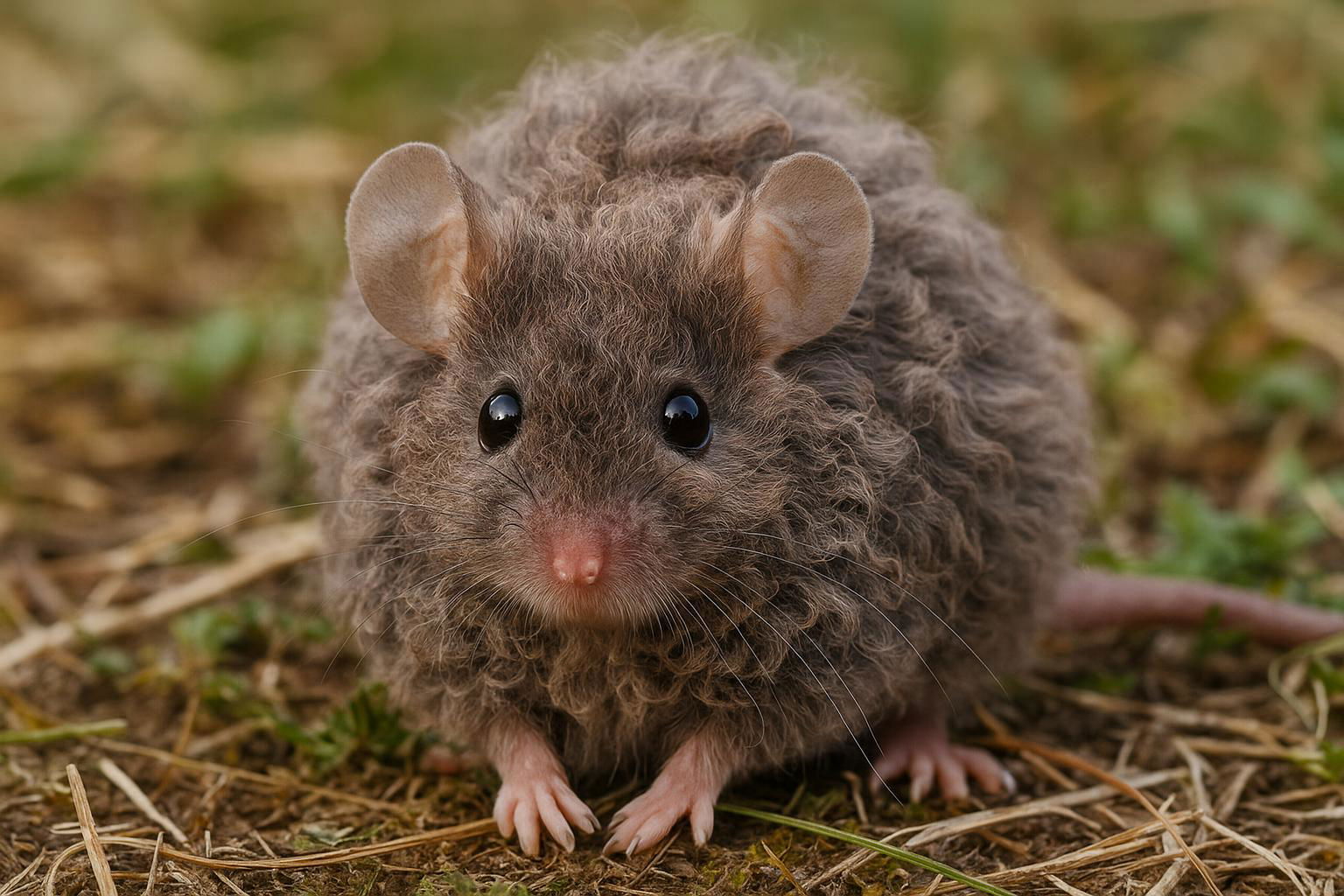
The house mouse, scientifically known as Mus musculus, is a small mammal belonging to the Rodentia order. It is one of the most widespread and adaptable mammals, found across various habitats worldwide due to its close association with human settlements. The house mouse is characterized by its small, rounded body, which typically measures between 7.5 to 10 cm in length, excluding the tail. Its fur is usually a uniform grayish-brown, but this can vary slightly depending on environmental factors.
House mice have large, rounded ears and a pointed snout, features that aid in their acute sense of hearing and smell, essential for their survival. They are primarily nocturnal creatures, exhibiting behaviors such as foraging and nesting that are ideally suited for a night-active lifestyle. Their diet is omnivorous but heavily leans on grains, seeds, and fruits, although they can adapt to consume food waste in urban environments.
Mus musculus is an opportunistic breeder with a well-developed reproductive system that allows for rapid population growth under favorable conditions. Females can produce multiple litters each year, with each litter averaging 5 to 8 young. In scientific contexts, the house mouse is renowned as a model organism in genetic research and biomedical studies due to its genetic and physiological similarities to humans. Its widespread presence and adaptability make the house mouse both a pest in domestic and agricultural settings and a valued subject in scientific research.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
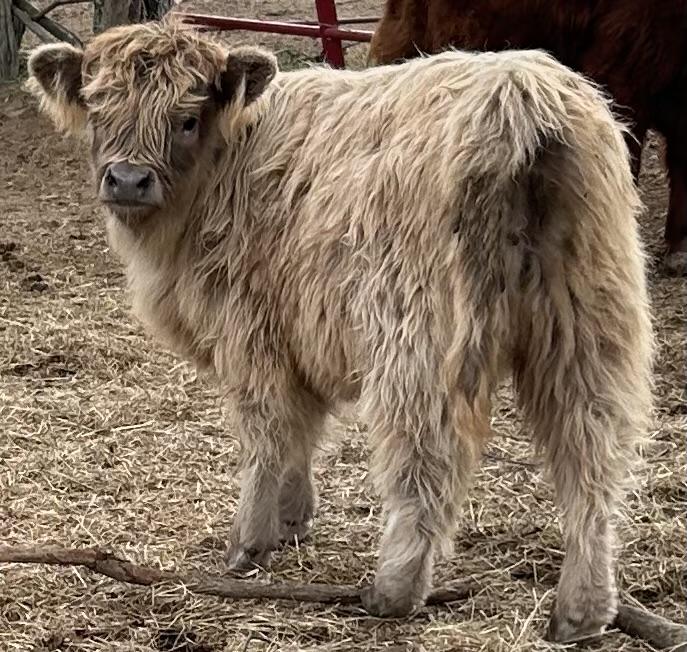
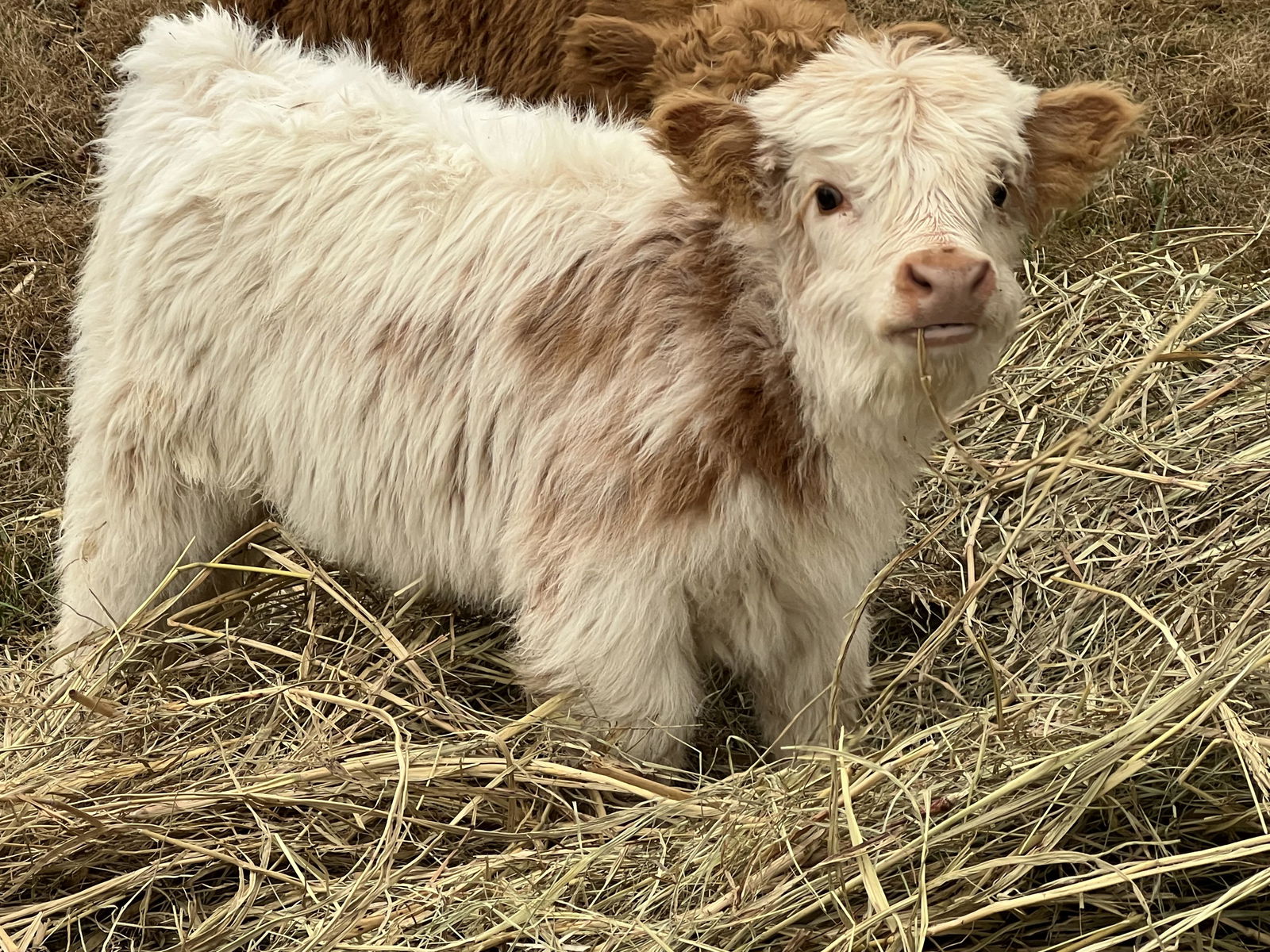
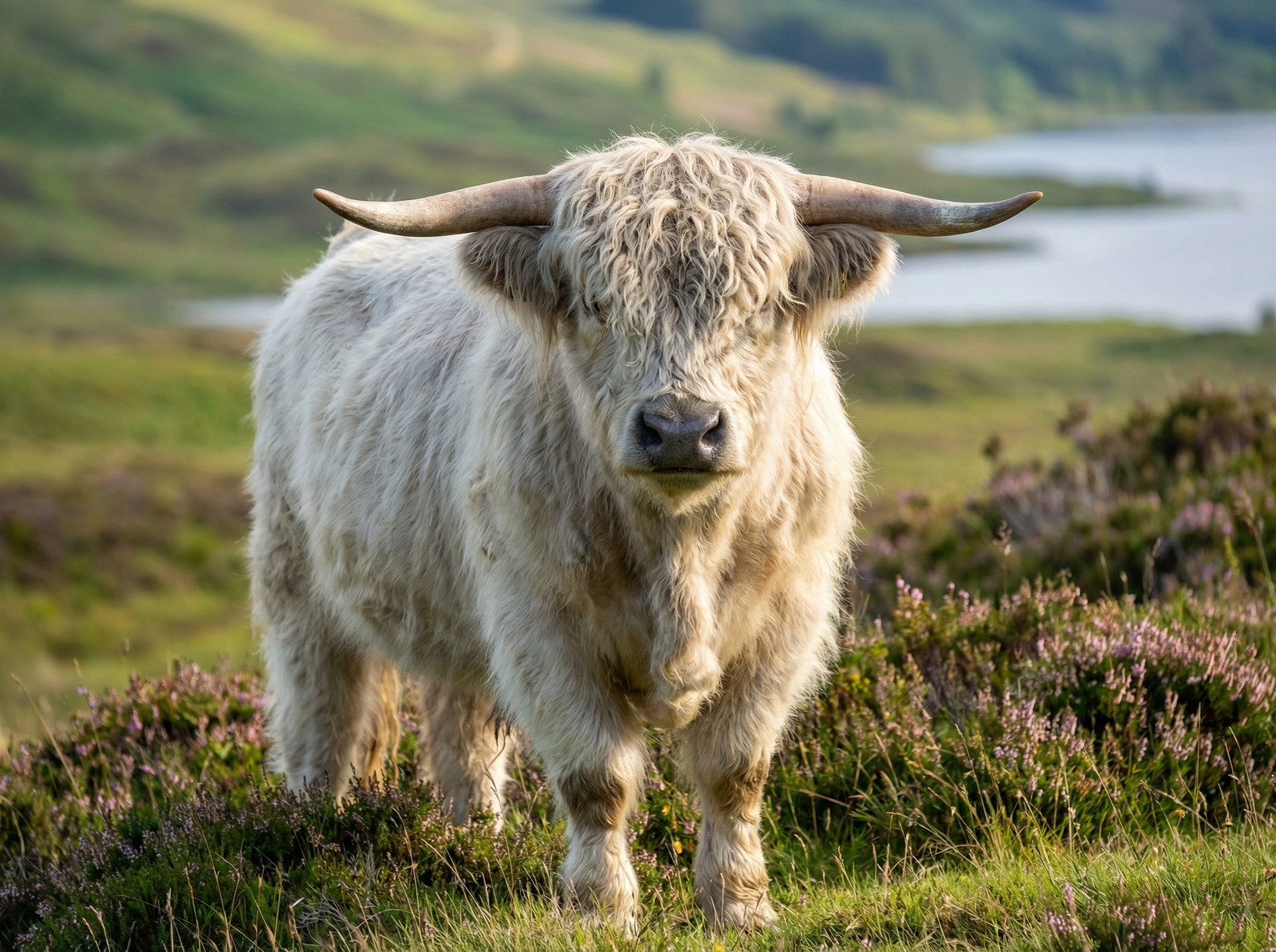 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
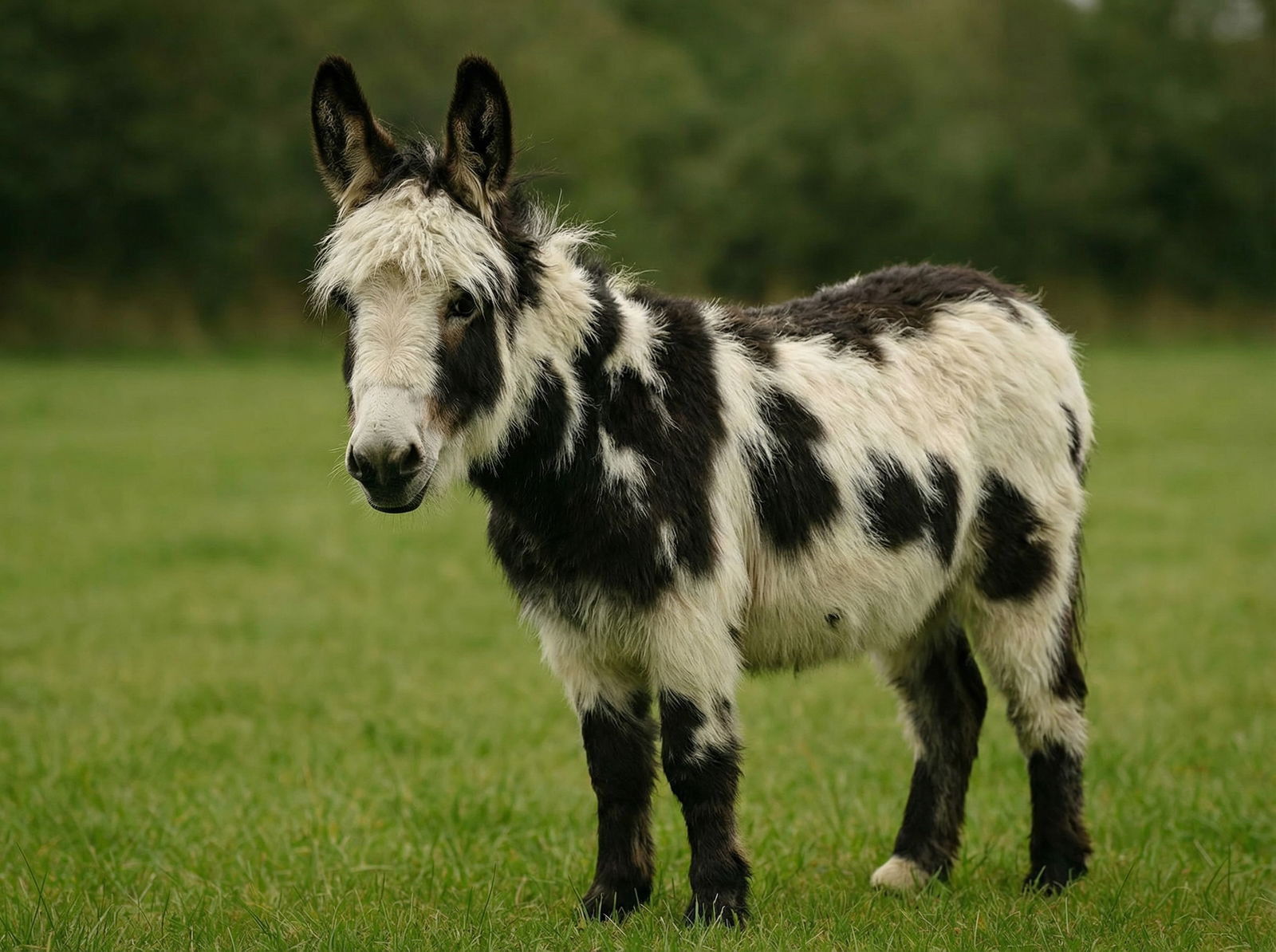 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
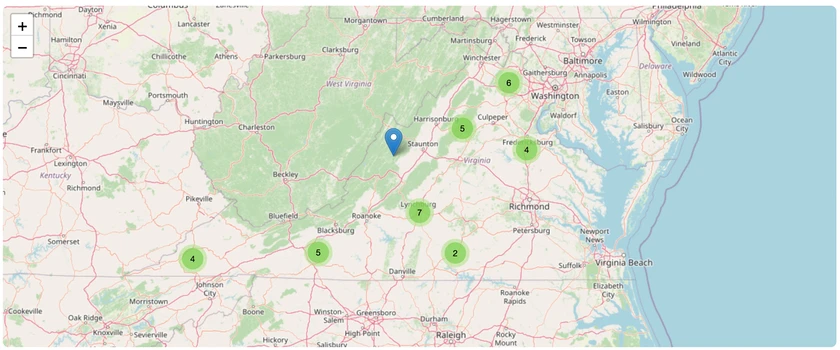 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
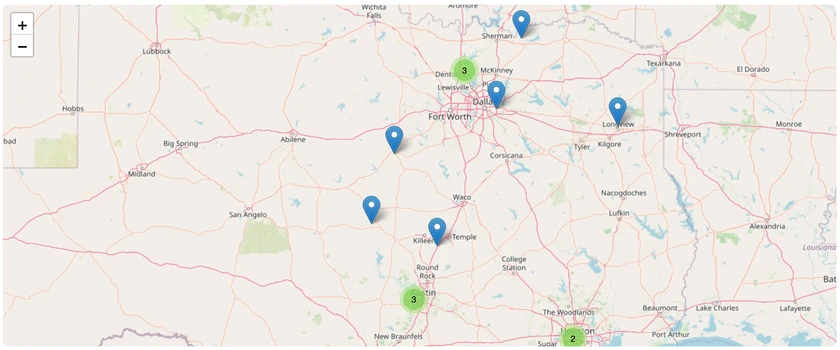 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas





















