White-Headed Capuchin
Cebus capucinus
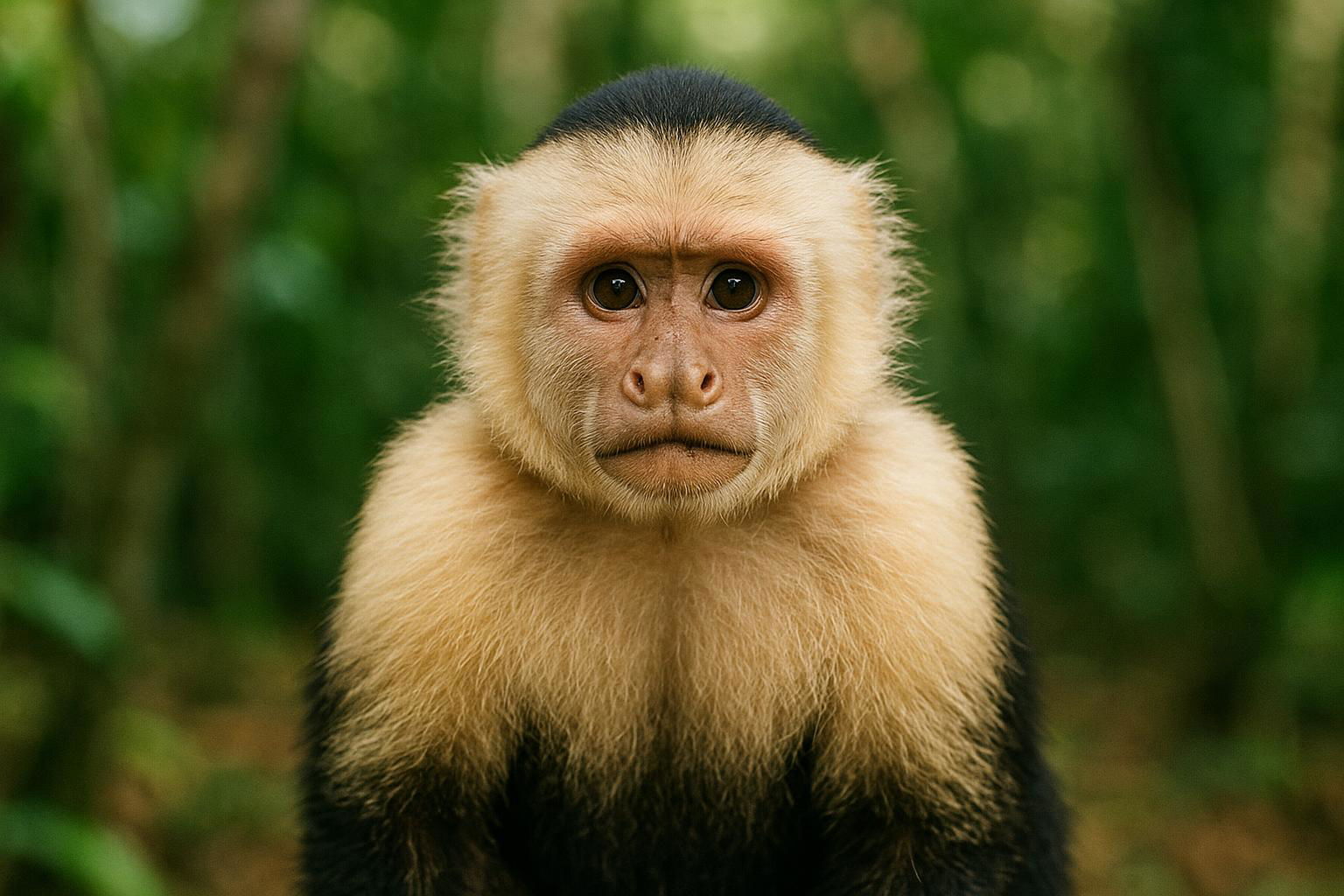
The White-Headed Capuchin, scientifically known as Cebus capucinus, is a lively and intelligent New World monkey native to the tropical forests of Central and South America. Characterized by its striking coloration, this primate features a cream or white face and chest contrasting with its dark brown or black body and limbs. Known for their agility, these capuchins navigate the forest canopy using their prehensile tails to expertly hang and swing through the trees. Their social structure is complex, with groups typically consisting of several females, their offspring, and a few male individuals.
Highly adaptable and intelligent, White-Headed Capuchins are omnivorous, feeding on a diverse diet that includes fruits, nuts, insects, small vertebrates, and even bird eggs. They are renowned for their problem-solving skills and use of tools, such as using stones to crack open hard nuts. These monkeys communicate using a range of vocalizations and gestures, which are crucial for maintaining social bonds and coordinating group activities. Despite being common in some areas, habitat loss and fragmentation pose significant threats to their populations, making habitat conservation crucial for their continued survival.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
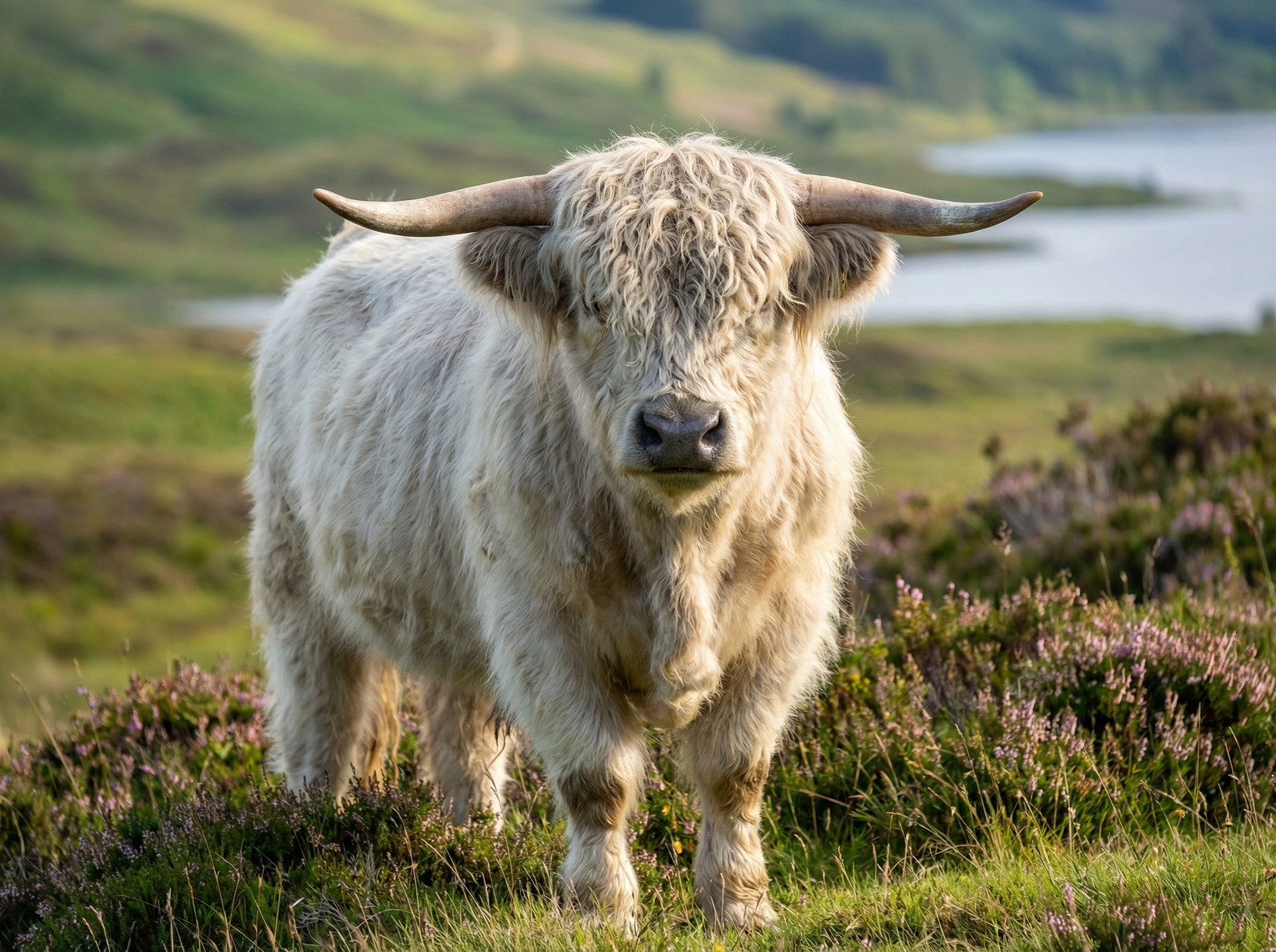 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
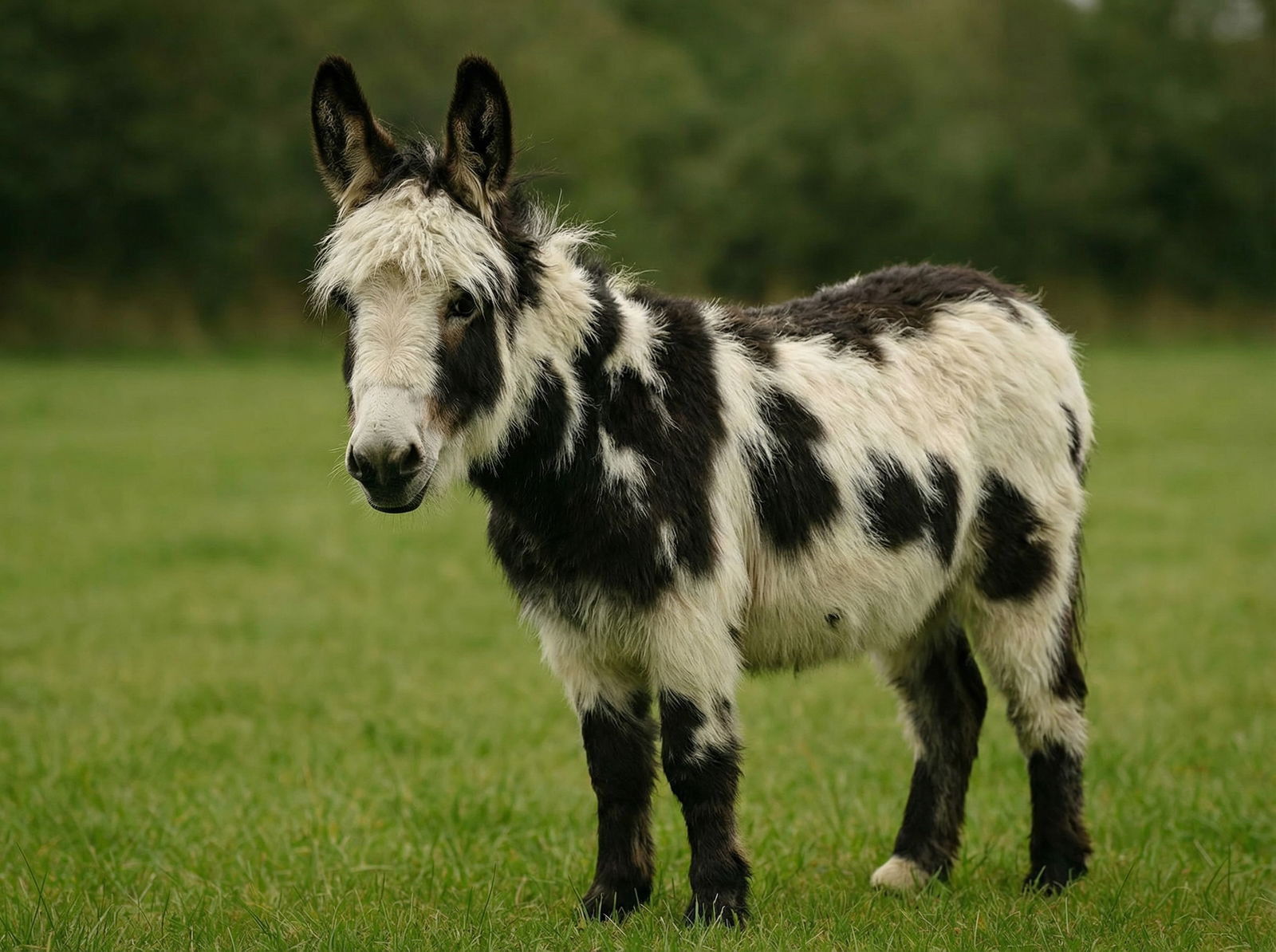 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












