Tigon
Panthera leo x Panthera tigris
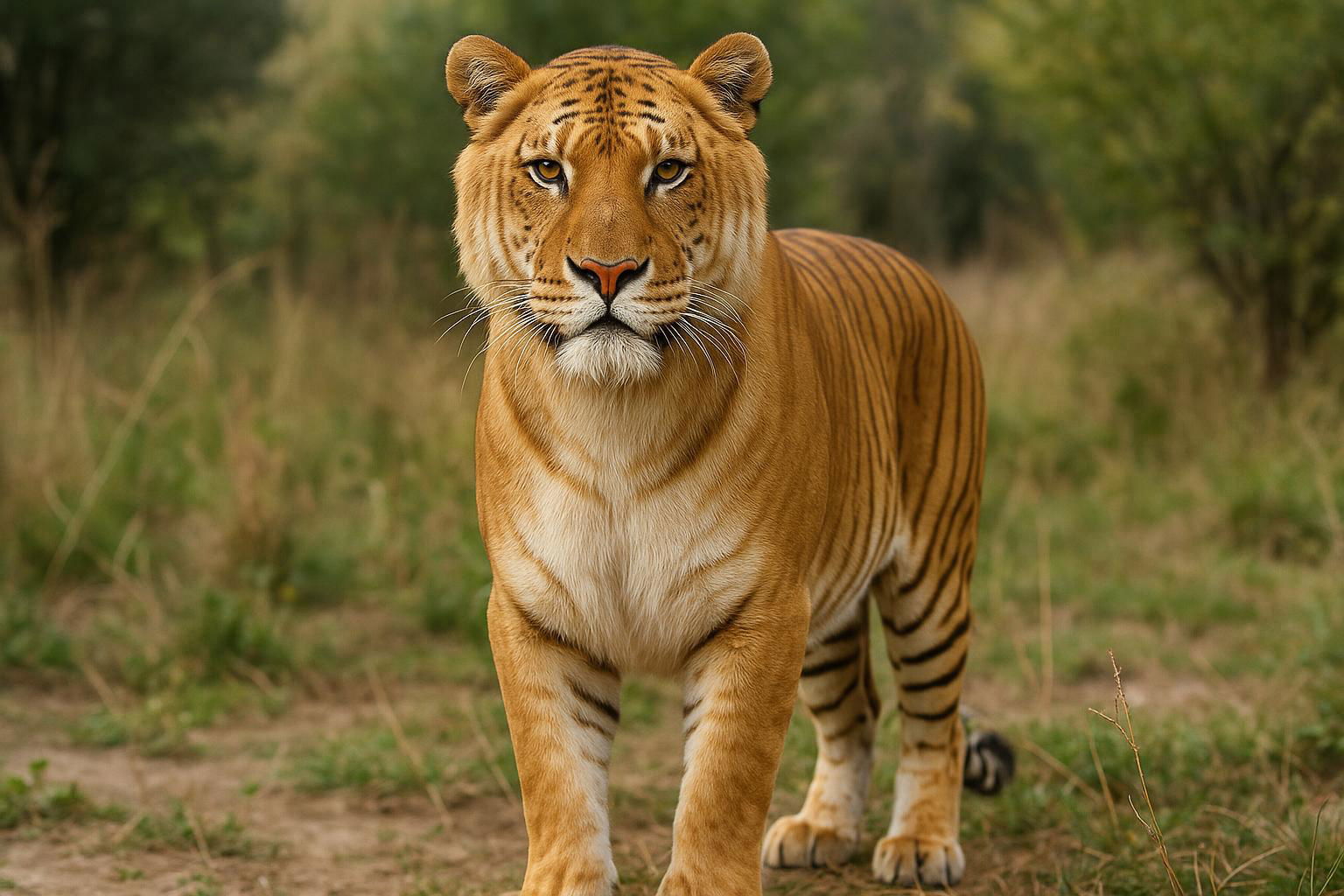
The Tigon, scientifically known as Panthera leo x Panthera tigris, is a hybrid big cat resulting from the crossbreeding of a male lion (Panthera leo) and a female tiger (Panthera tigris). Bearing characteristics from both parents, Tigons typically inherit a mix of physical and behavioral traits. They often exhibit a striking appearance with a lion-like mane that is less pronounced, coupled with the distinct striping pattern of a tiger on their fur. Their coats may display a unique blend of tan, orange, and brown hues, with variations in striping intensity.
Tigons tend to be smaller than their hybrid counterpart, the Liger, as well as both parent species, due to a phenomenon called growth dysregulation caused by the hybridization. These animals are known for their playful and gentle nature, traits reminiscent of both lions and tigers, though they may also exhibit a strong predatory instinct. Typically found in captivity, where they are bred intentionally, Tigons are rare in the wild due to the geographic separation of their parent species and differences in natural habitats.
Due to their hybrid status, Tigons face challenges in terms of health and reproduction, with some individuals experiencing genetic issues that can affect longevity and fertility. Nonetheless, they have a unique charm and contribute to our understanding of genetics and species interaction. Tigons are a testament to the fascinating, albeit controversial, world of hybrid animals, showcasing the beauty and complexity of nature's diversity.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
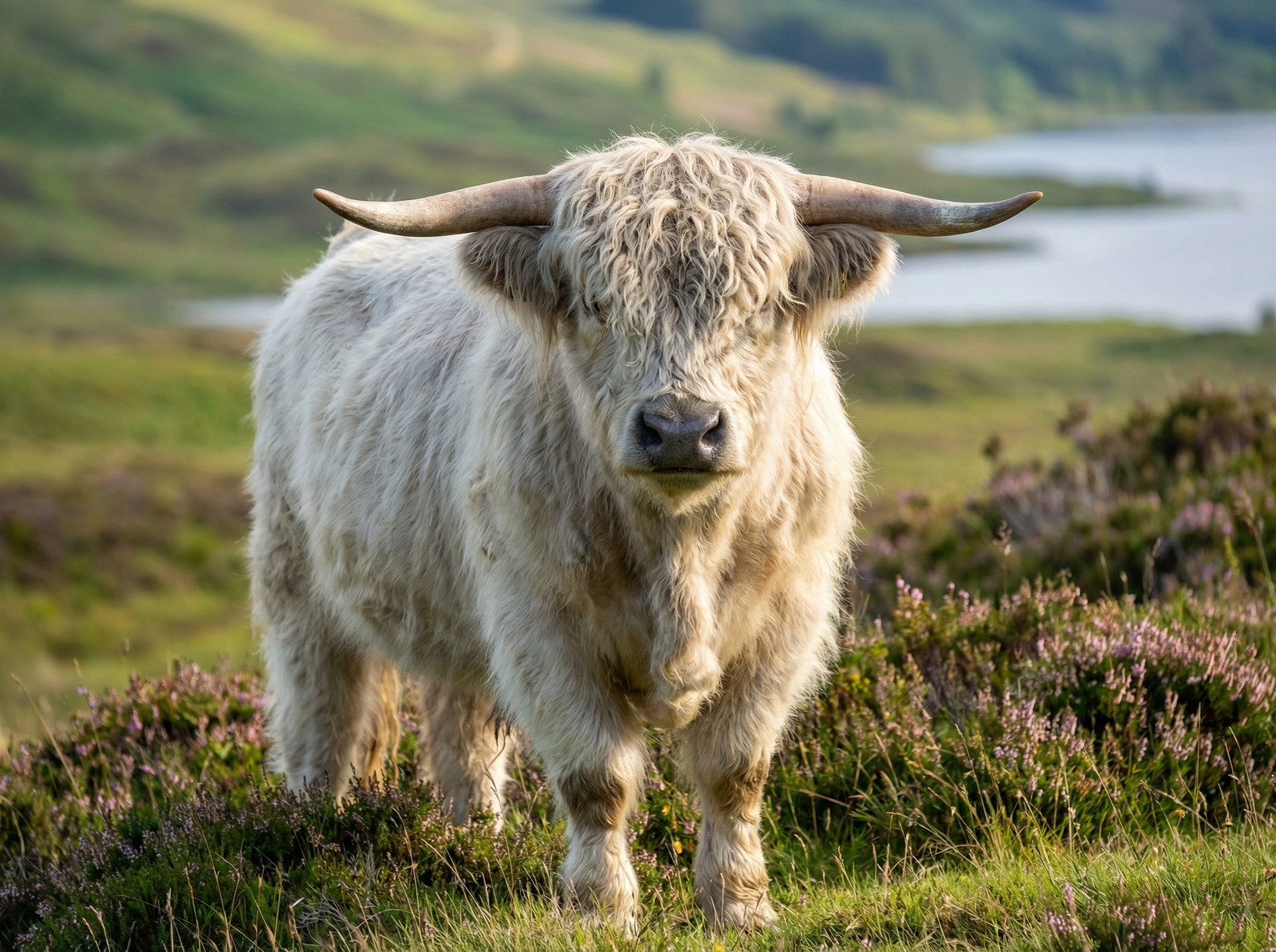 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
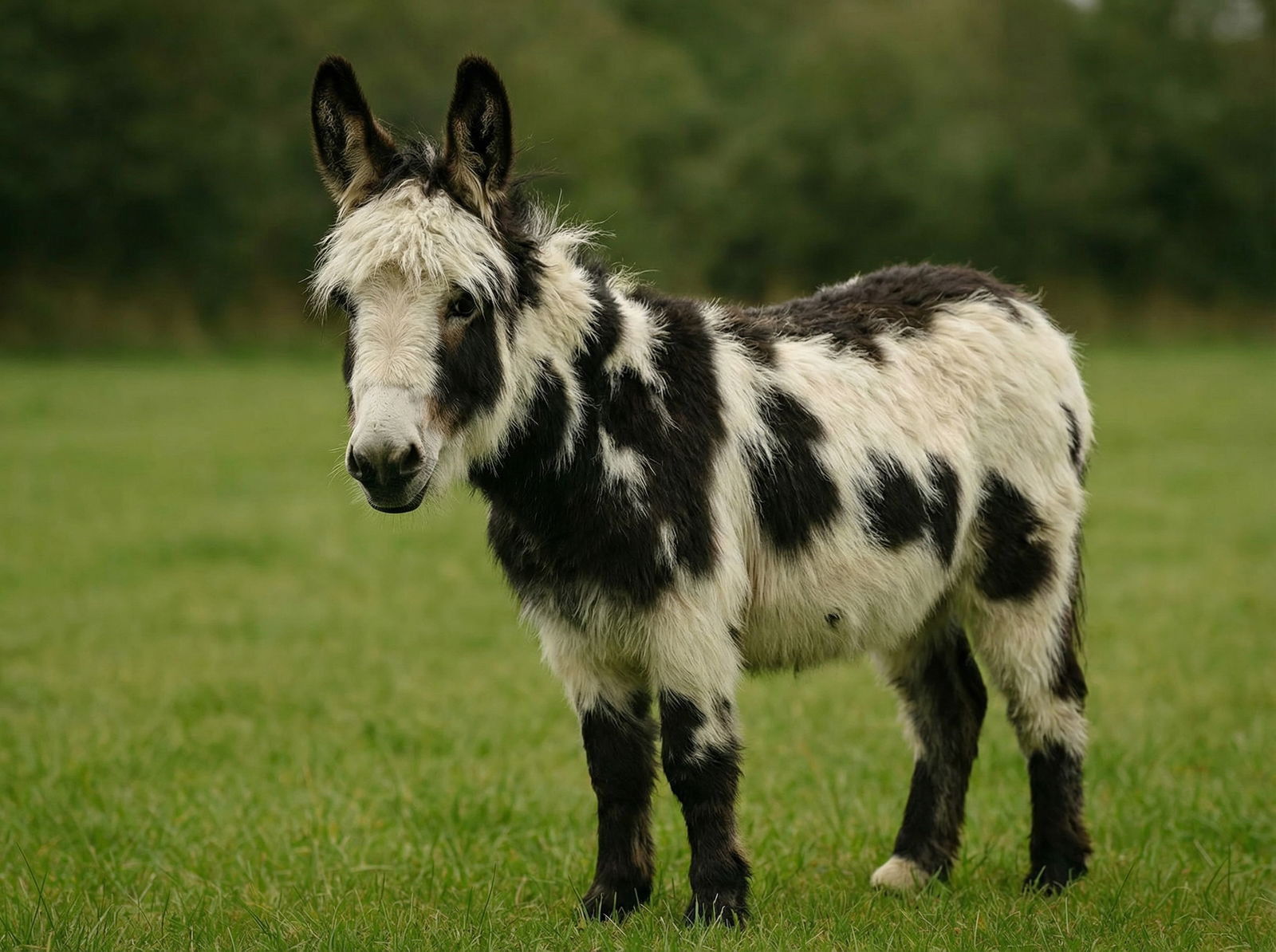 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
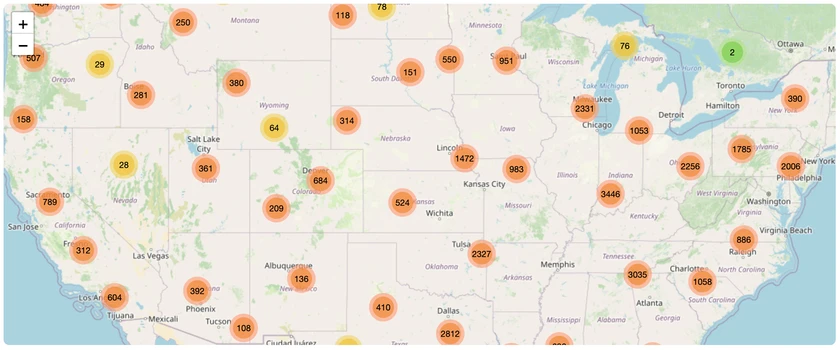 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
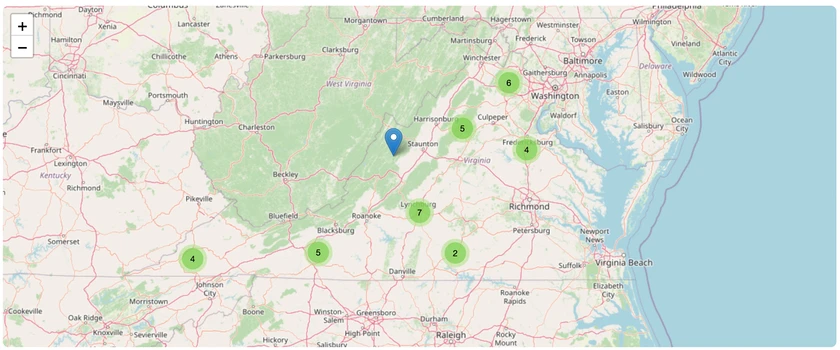 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
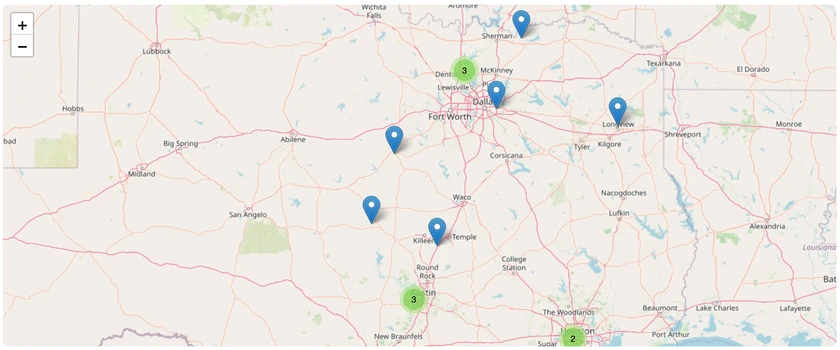 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












