Rusa Deer
Rusa timorensis
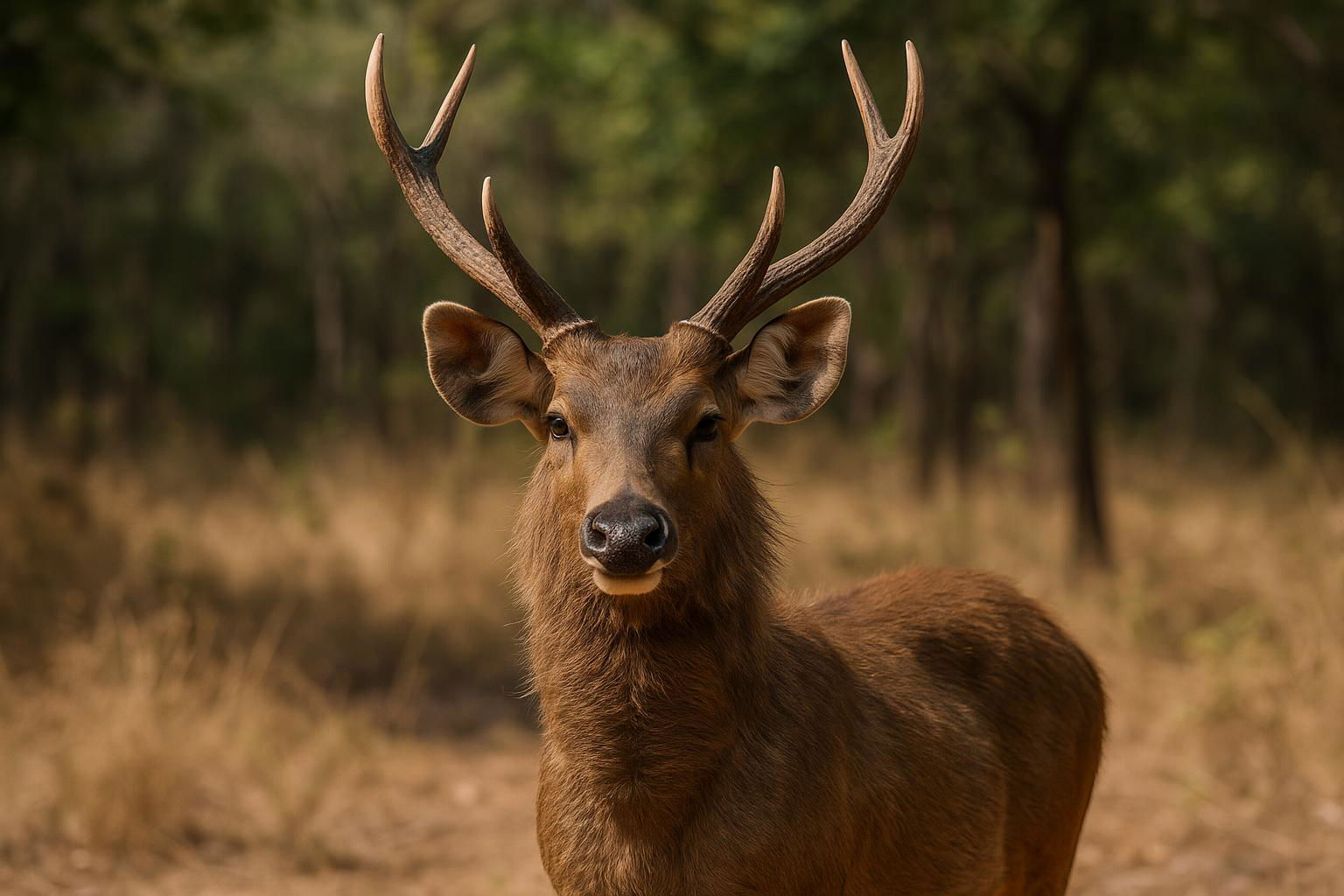
The Rusa Deer, scientifically known as Rusa timorensis, is a striking species indigenous primarily to the islands of Indonesia and Timor-Leste, with introduced populations in Australia and New Caledonia. This elegant creature stands out with its robust and sturdy build, balancing on slender yet powerful legs, which contribute to its agile movements. The coat of the Rusa Deer is generally a shade of sandy grey or brown, providing effective camouflage within its natural habitat of dense forests, grasslands, and wetlands.
Male Rusa Deer, known as stags, are notable for their majestic, three-tined antlers which they shed and regrow annually, growing larger and more elaborate with each year. During the breeding season, known as the rut, stags are known for their loud, distinctive calls and display behaviors to assert dominance and attract females, or hinds.
Typically, these herbivorous mammals forage in the twilight hours, feeding on a diet that includes grasses, leaves, and fallen fruits. Socially dynamic, Rusa Deer often form small herds consisting of females and their young, while males tend to be more solitary or form bachelor groups outside of the breeding season.
In their ecosystems, Rusa Deer play a vital role in maintaining the balance of vegetation, although their populations are at times subject to pressures from habitat loss and competition with livestock. Conservation efforts continue to monitor and support this species, ensuring that these deer remain a captivating presence in their natural environments.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
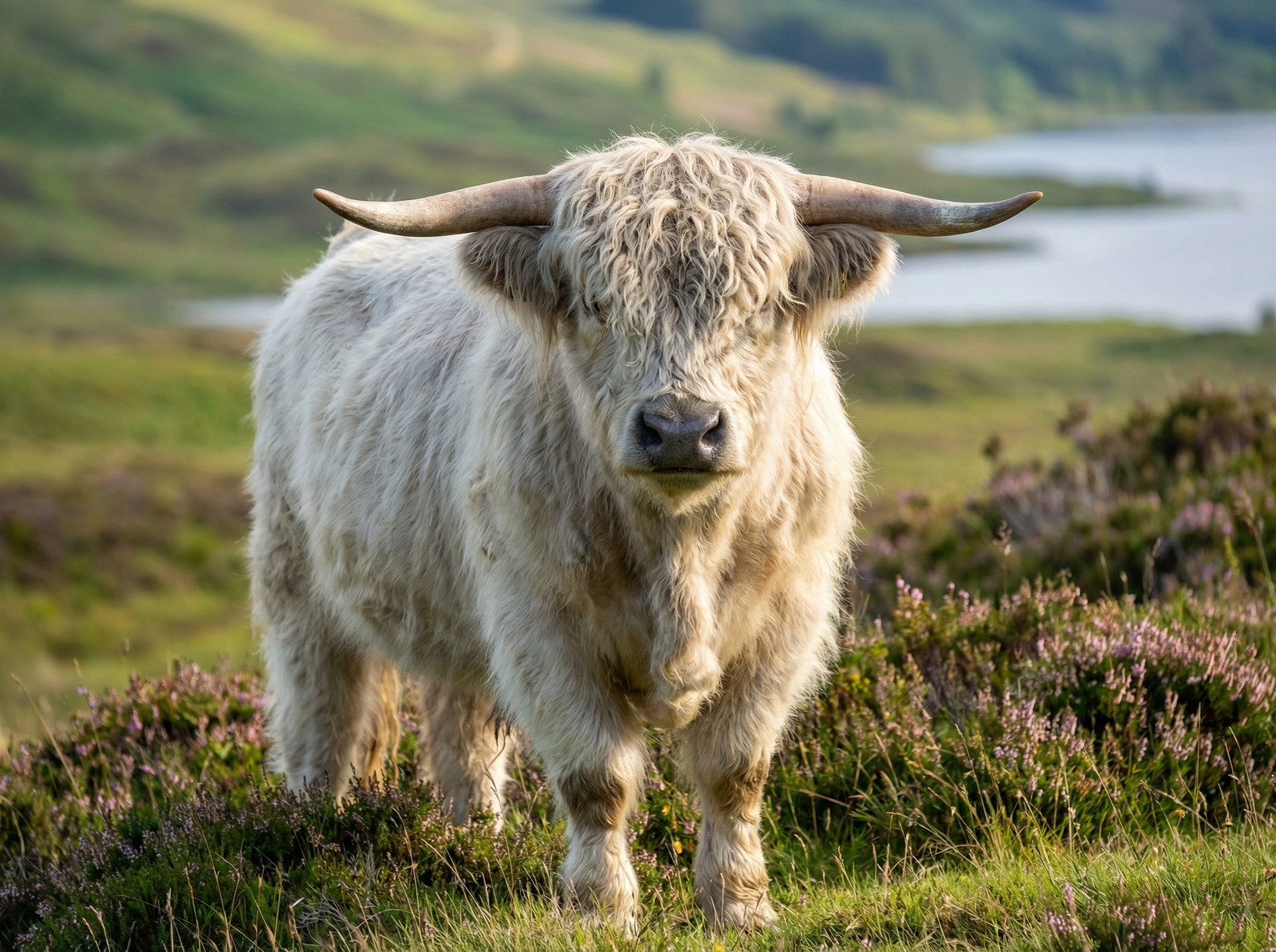 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
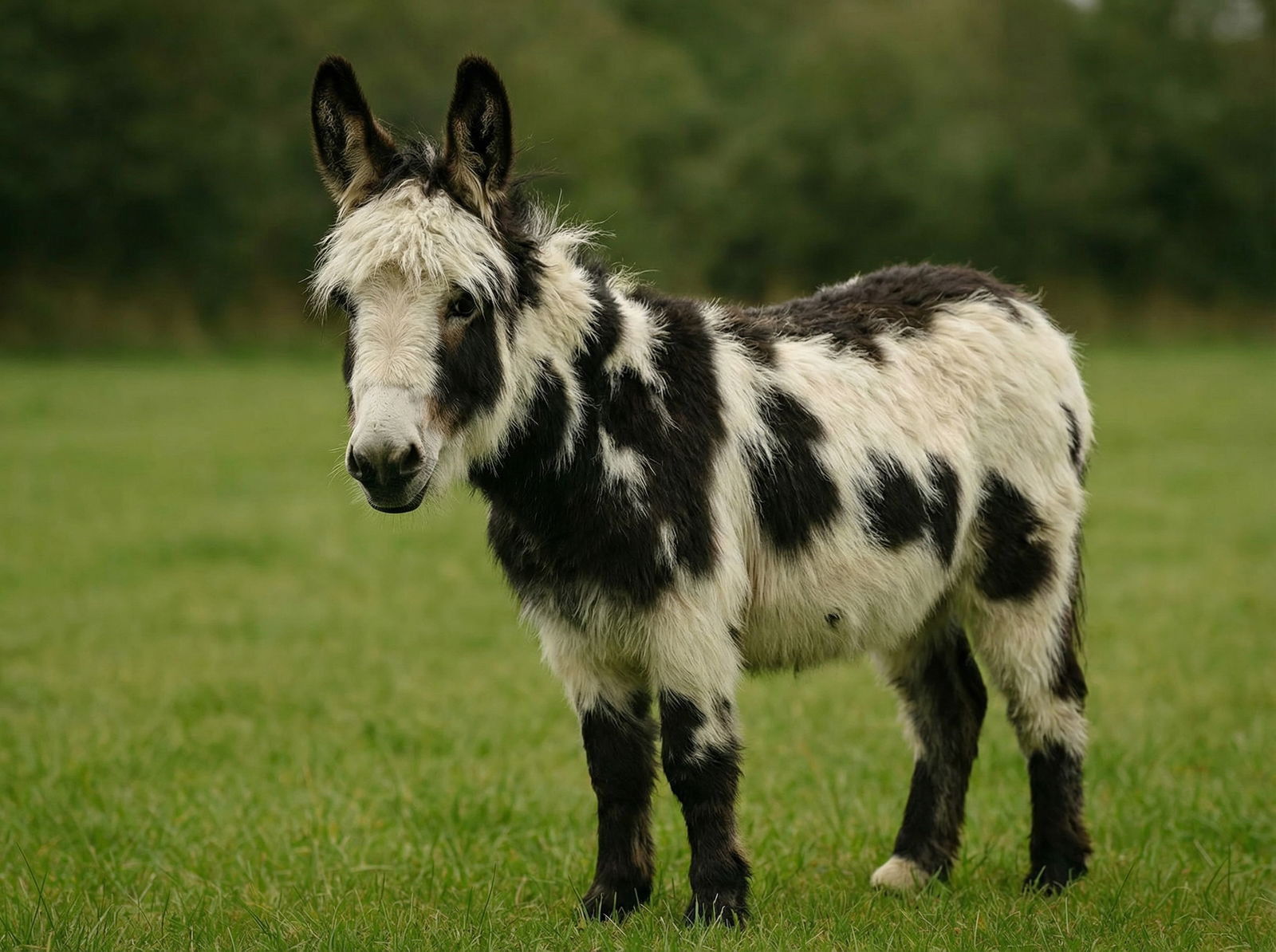 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
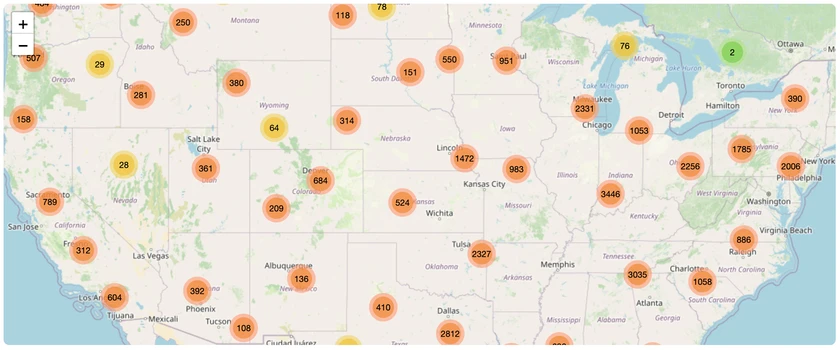 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
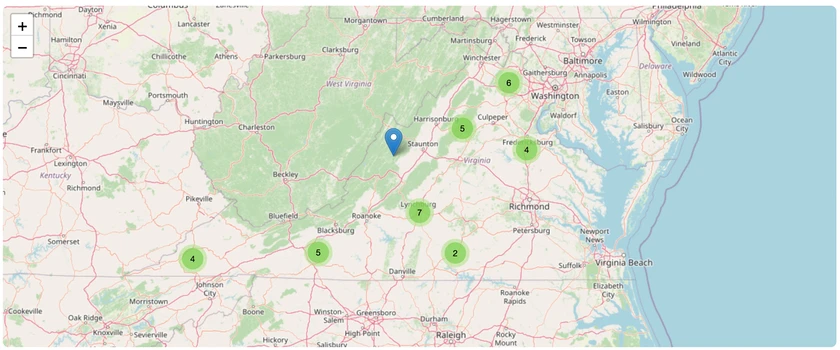 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
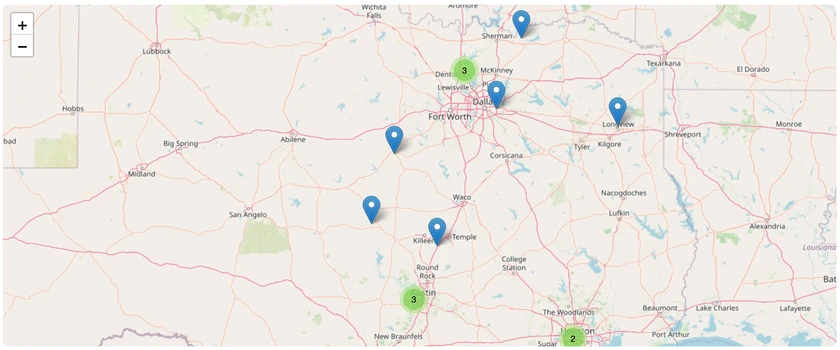 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












