Gunnison'S Prairie Dog
Cynomys gunnisoni
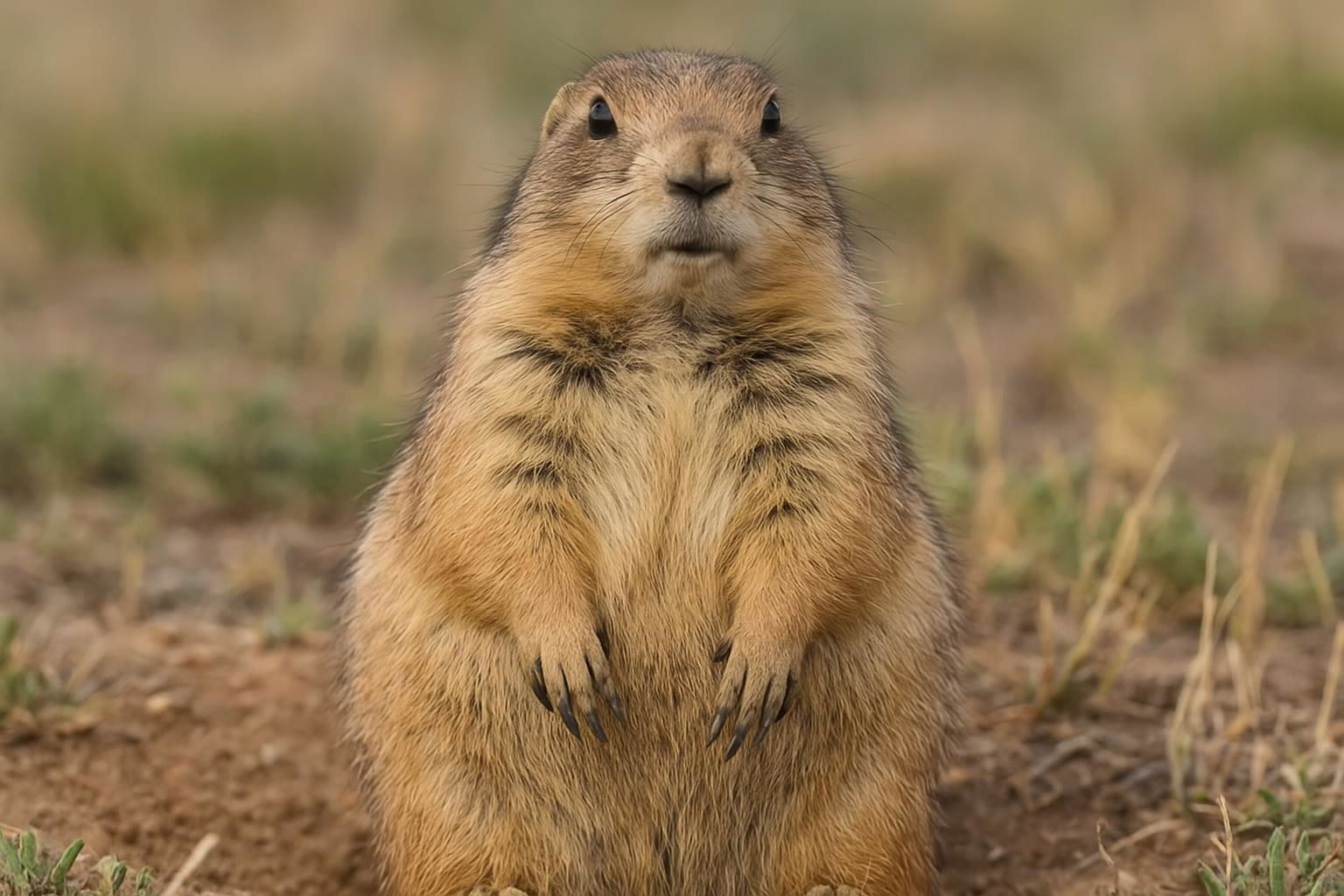
Gunnison's Prairie Dog (Cynomys gunnisoni) is a small, burrowing rodent native to the grasslands and shrublands of the American Southwest, specifically found in parts of Colorado, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico. It is one of five species of prairie dogs, recognizable by its stout body, short tail, and tan fur with lighter underparts. Adults typically range from 12 to 14 inches in length and weigh between 1.5 to 2.5 pounds. Known for their complex social structures, Gunnison's Prairie Dogs live in colonies or "towns" consisting of elaborate tunnel systems that provide protection and facilitate social interaction.
These highly vocal animals communicate through a sophisticated system of calls to alert each other of potential predators, which can include hawks, coyotes, and snakes. Their diet primarily consists of grasses, herbs, and seeds, playing a crucial role in their ecosystem by aerating the soil and influencing plant distribution. Though they are considered a keystone species, their populations have been threatened by habitat destruction, disease, and eradication programs. Conservation efforts are critical to preserving their role in maintaining biological diversity and ecosystem health.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
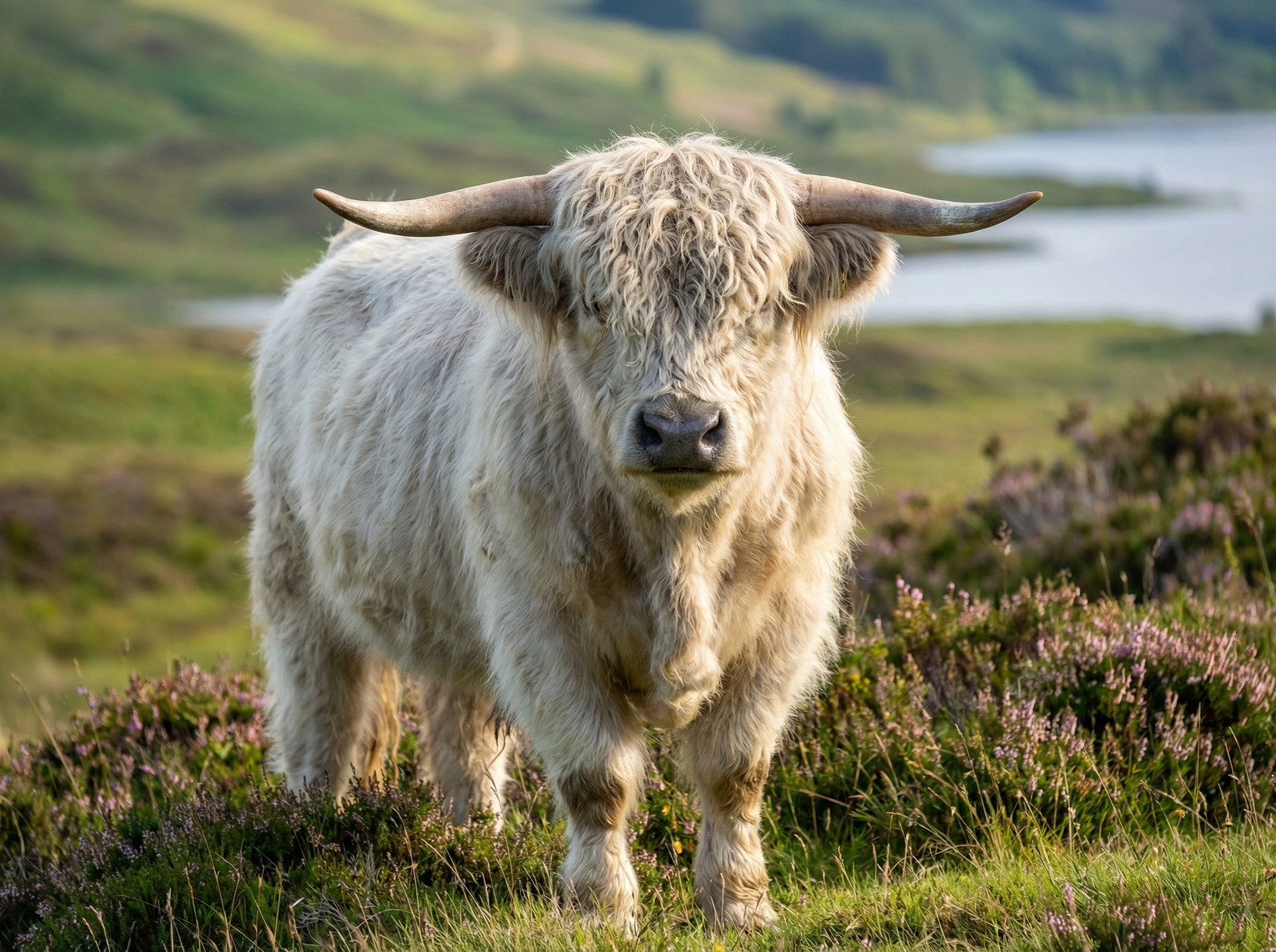 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
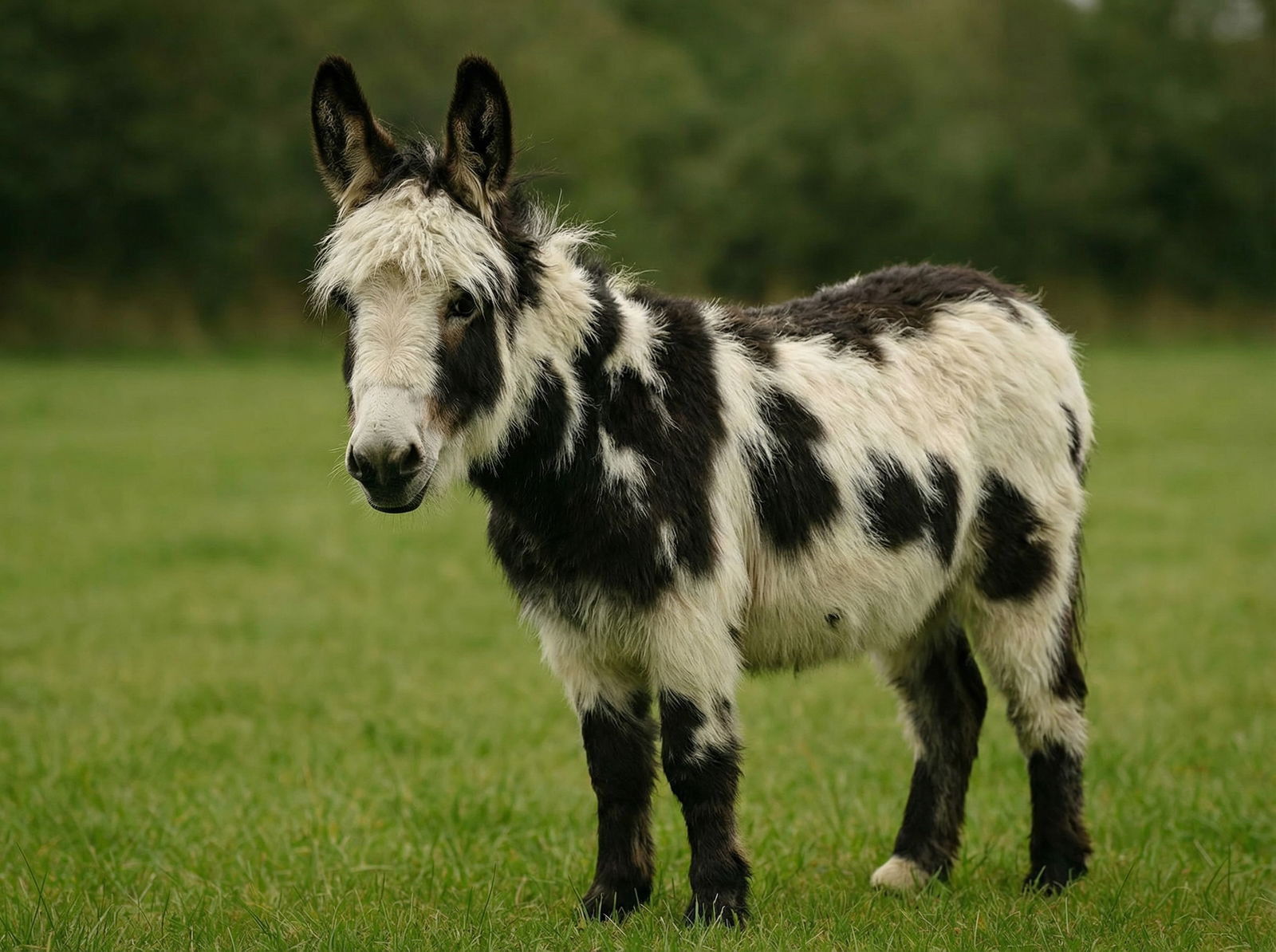 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
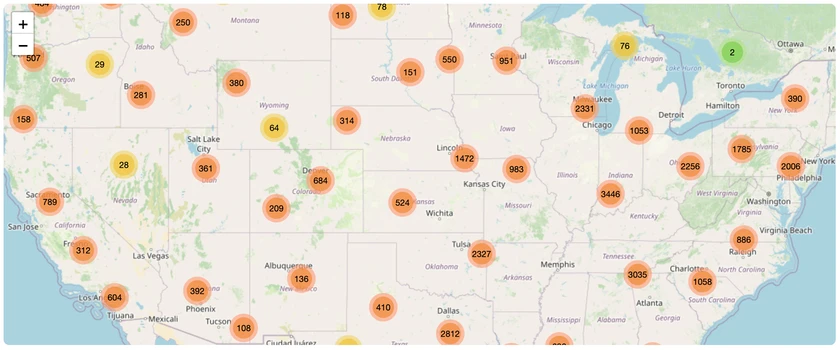 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
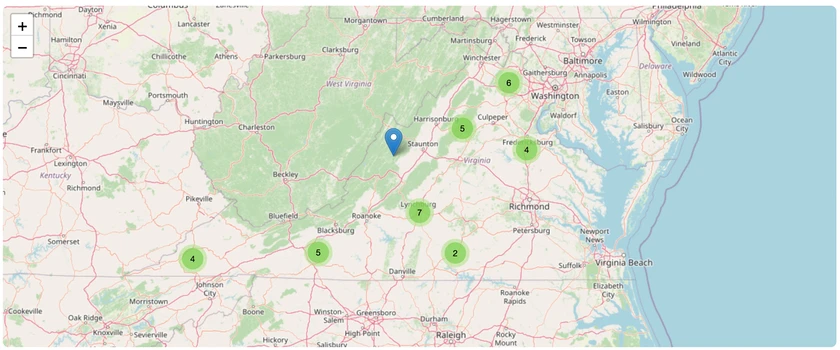 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
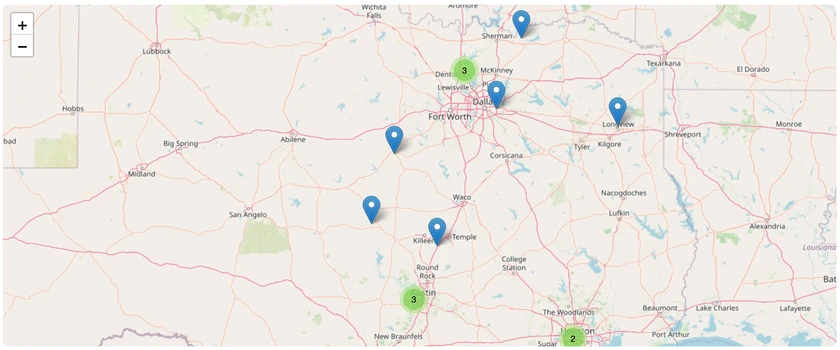 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












