Fire-Bellied Toad
Bombina orientalis
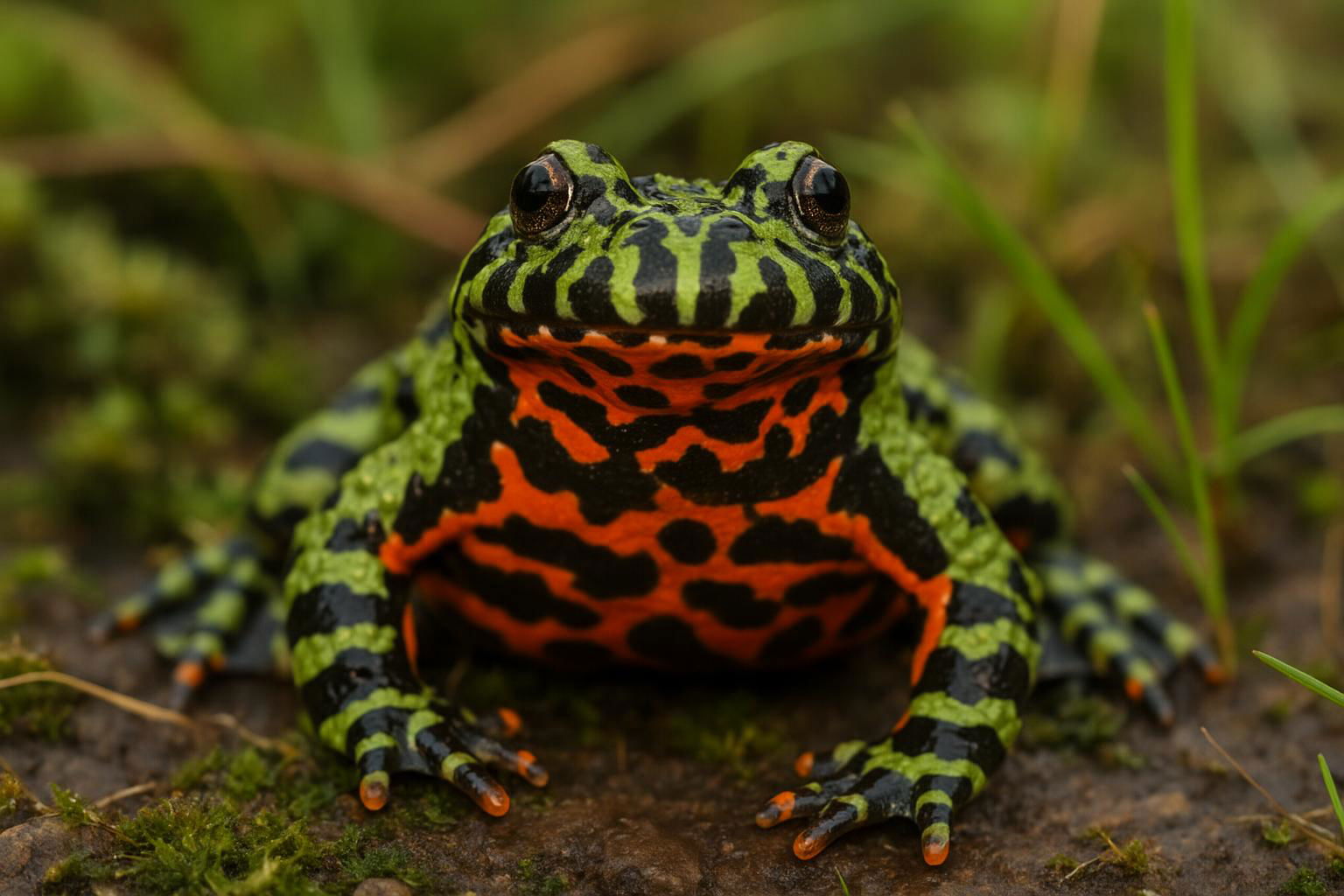
The Fire-Bellied Toad (Bombina orientalis) is a small, distinctive amphibian native to the forests, marshes, and river valleys of northeastern Asia, including regions of China, Korea, and Russia. Measuring between 4 and 5 centimeters in length, this toad is celebrated for its vibrant, eye-catching coloration. Its dorsal surface is typically mottled in shades of green or brown, providing camouflage in vegetation, while the underside displays a striking fiery orange or red with irregular black markings. This vivid ventral pattern acts as a warning to potential predators about its toxic skin secretions.
Fire-Bellied Toads are semi-aquatic and prefer a habitat that juxtaposes water bodies with ample vegetation, where they hunt for a diet of small insects, worms, and other invertebrates. Notably, these toads exhibit a unique locomotion style that combines swimming, hopping, and walking, earning them the description of being somewhat awkward on land yet proficient swimmers.
Social creatures, Fire-Bellied Toads are often seen in groups, and their breeding season is marked by vocal choruses of males calling to attract females. The amplexus is their mode of reproduction, where eggs are laid in shallow water and undergo external fertilization. Offspring emerge as tadpoles, undergoing a metamorphosis lasting several months.
Adaptable and fairly resilient, Bombina orientalis is a popular species within the exotic pet trade, though it requires specific care to replicate its natural habitat and maintain health. While not currently listed as endangered, its natural populations are susceptible to habitat loss and environmental changes, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
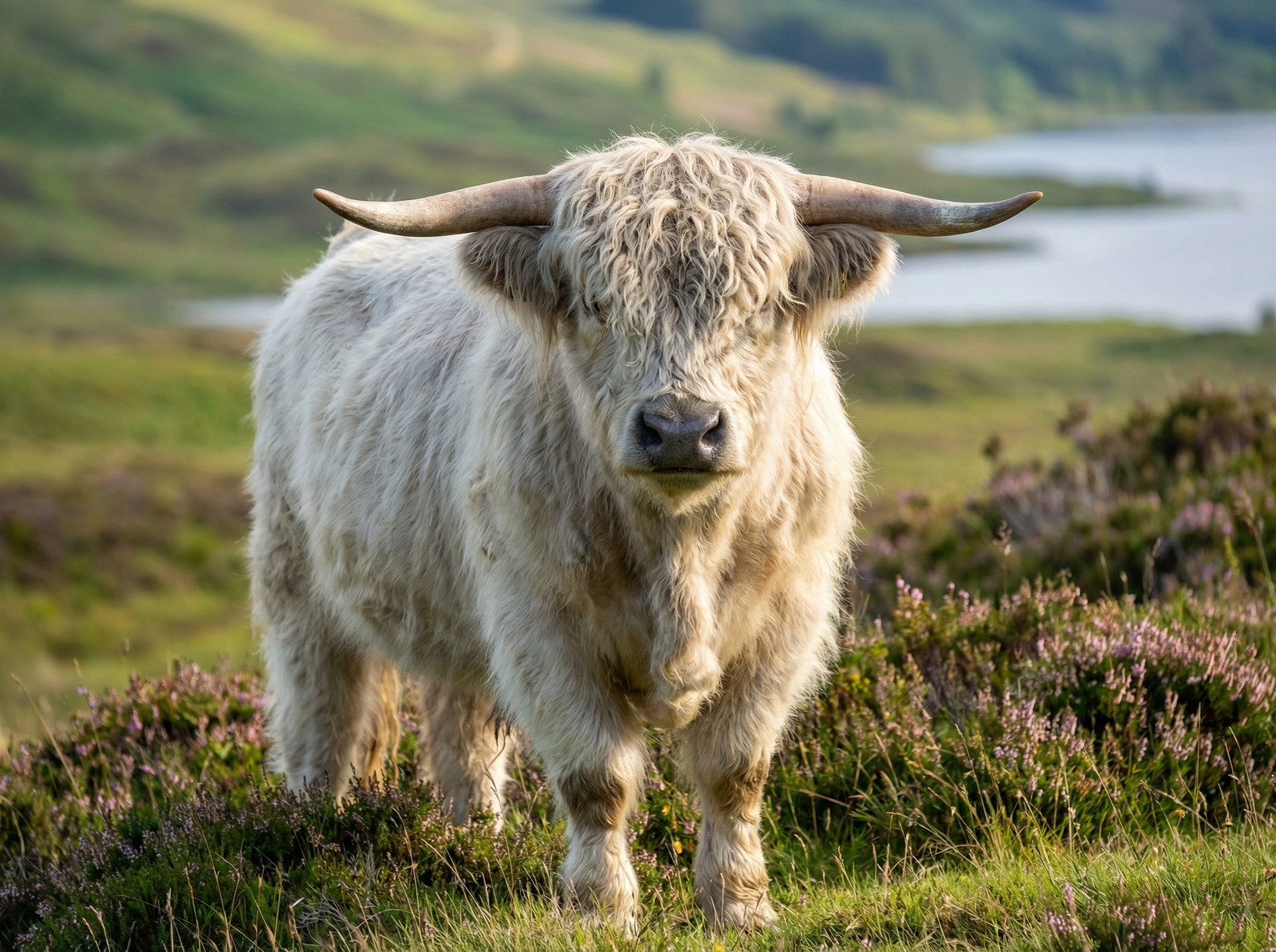 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
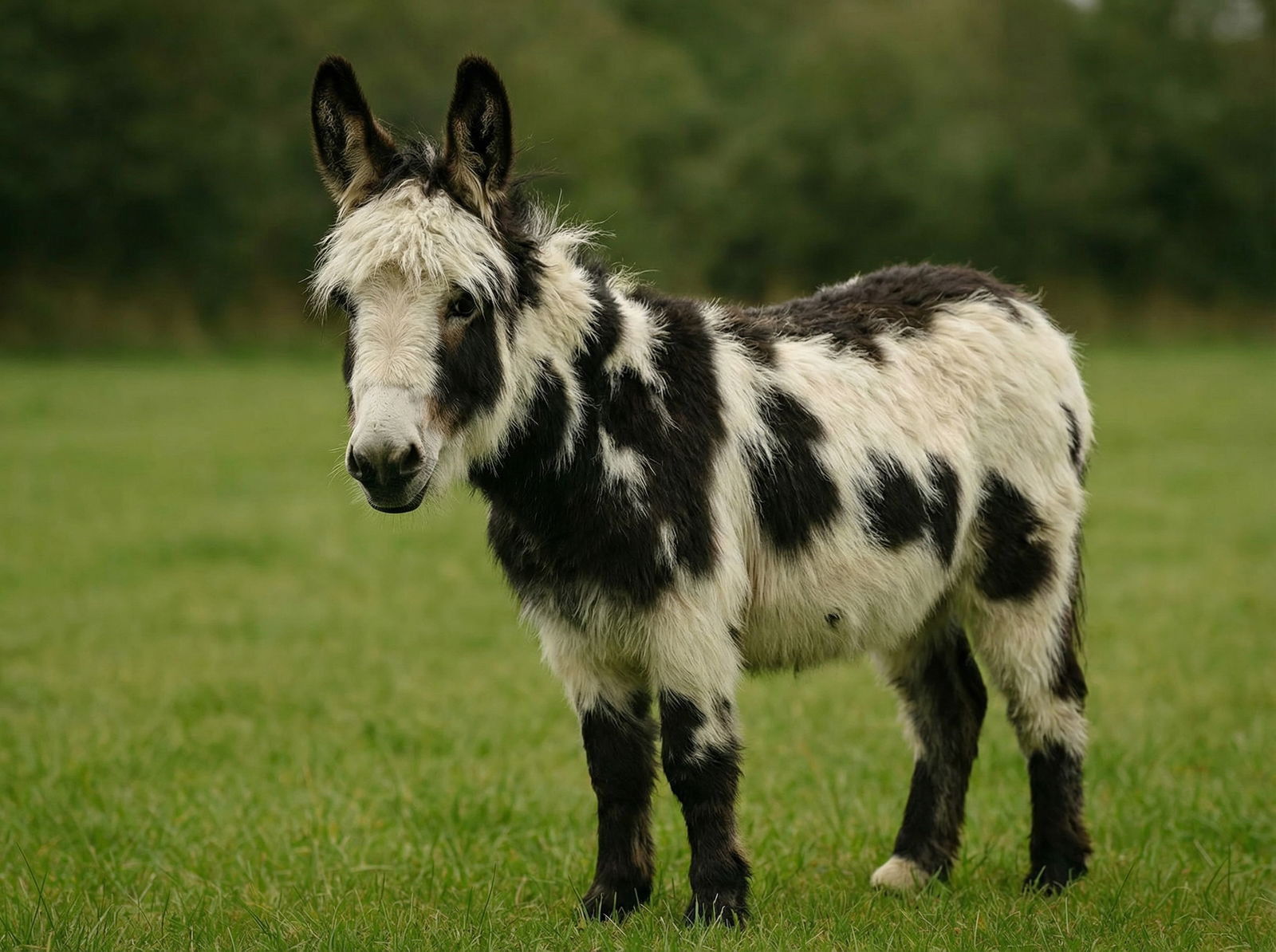 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
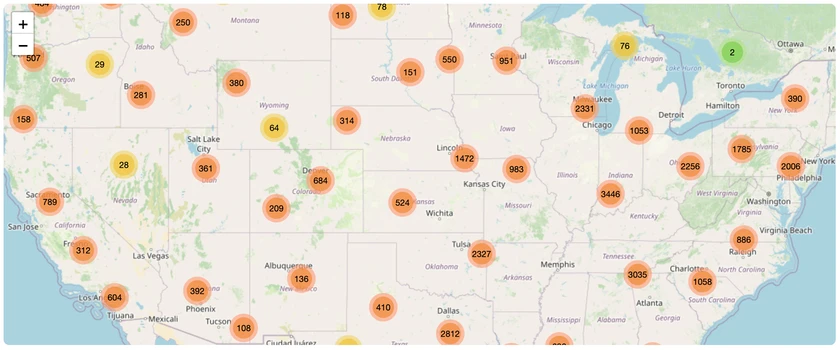 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
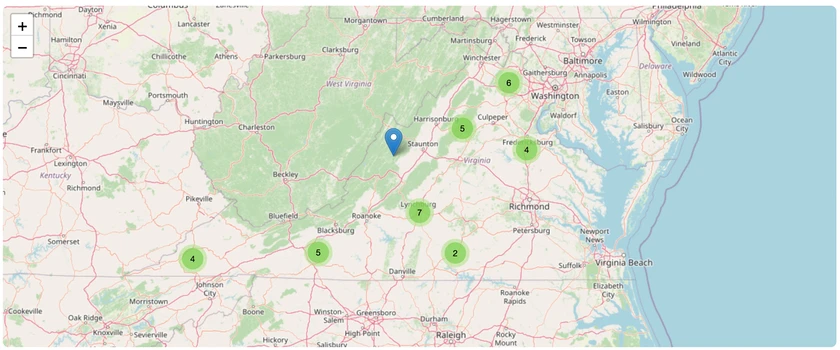 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
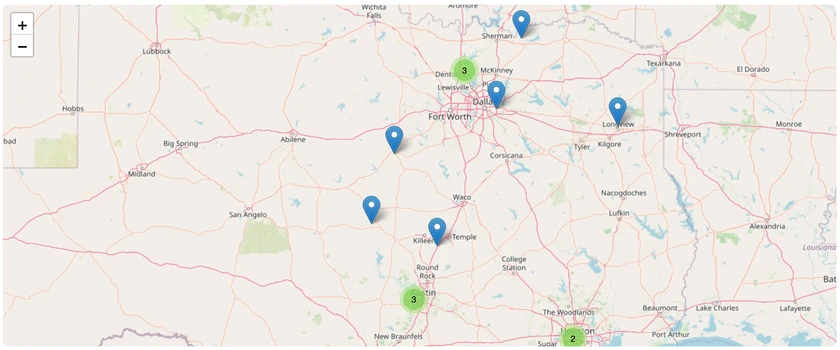 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












