Bonobo
Pan paniscus
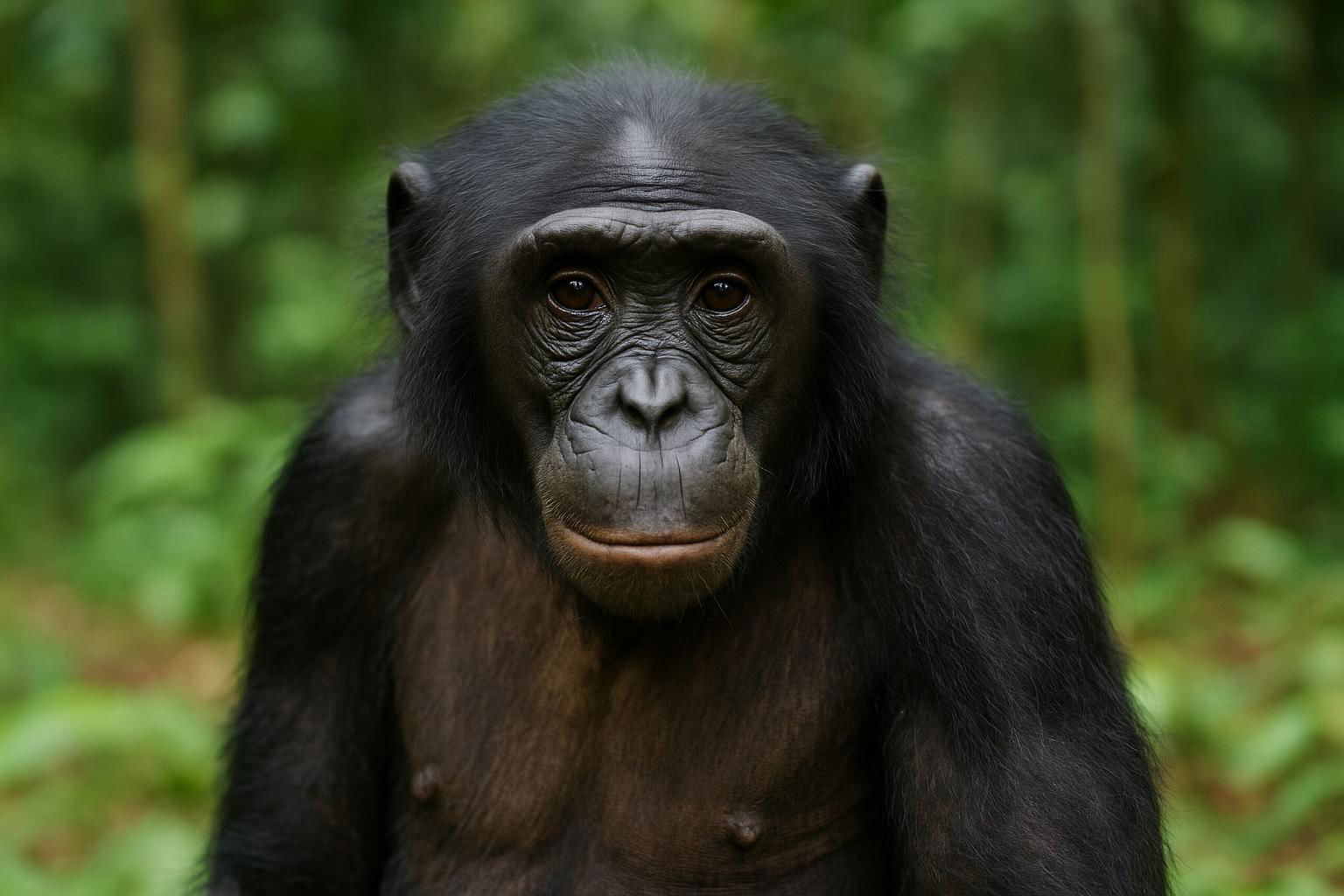
The Bonobo (Pan paniscus), also known as the pygmy chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus Pan, the other being the more widely known common chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes). Native to the dense, humid rainforests south of the Congo River in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, bonobos are distinguished by their slender builds, relatively long legs, and dark faces framed by tufts of hair. With a more peaceful and cooperative social structure compared to their chimpanzee counterparts, bonobos exhibit complex social behaviors characterized by strong matriarchal societies. They are known for their high degree of empathy, altruism, and the use of sexual behaviors as a means of social bonding and conflict resolution. Bonobos primarily feed on fruits, but their diet also includes leaves, small vertebrates, and insects. These intelligent primates are highly vocal and use a series of vocalizations to communicate, showcasing their advanced cognitive abilities. Conservation efforts are crucial for the bonobo, as they face threats from habitat destruction and poaching.
Colors: Wild Type
 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
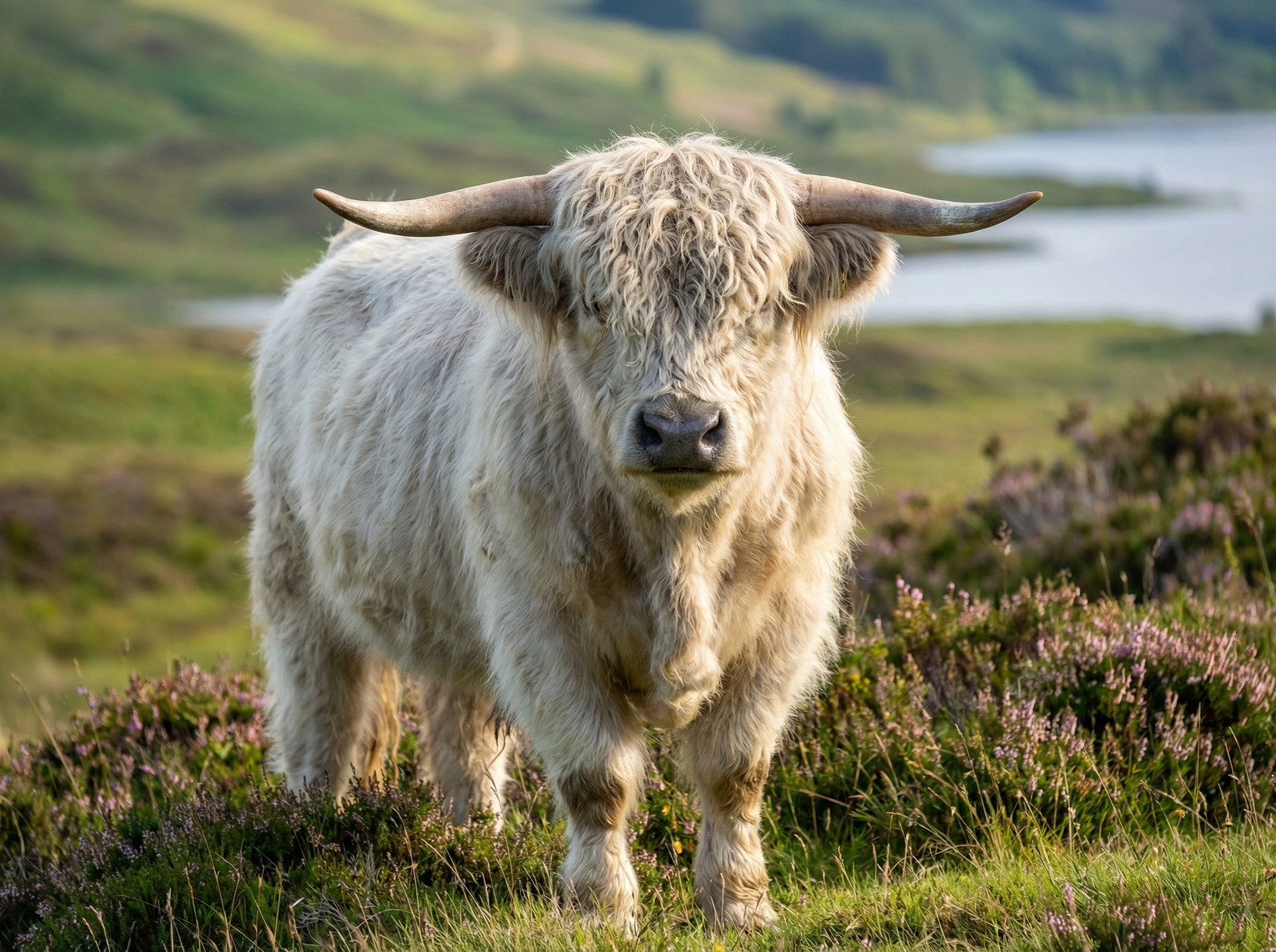 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
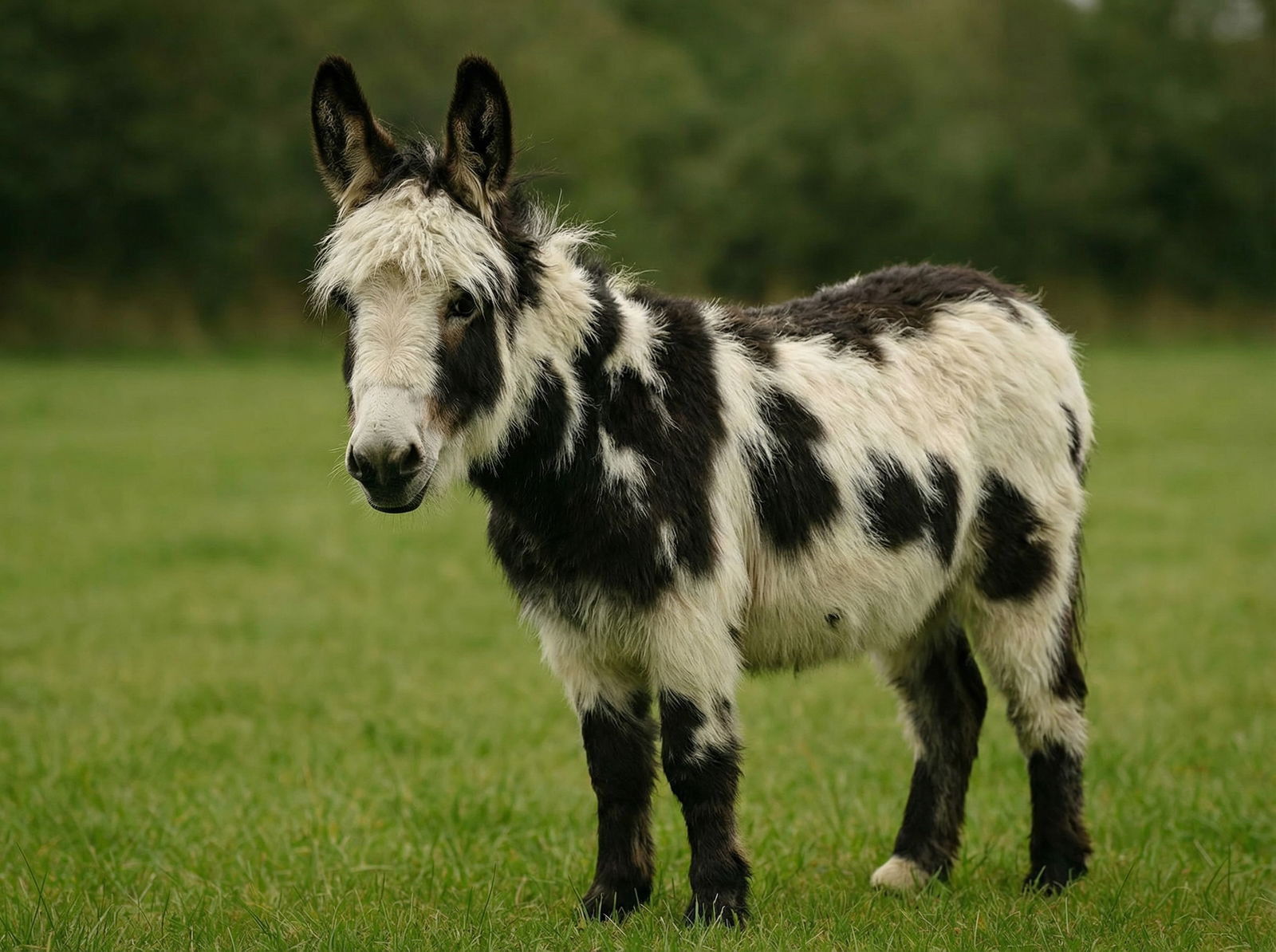 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
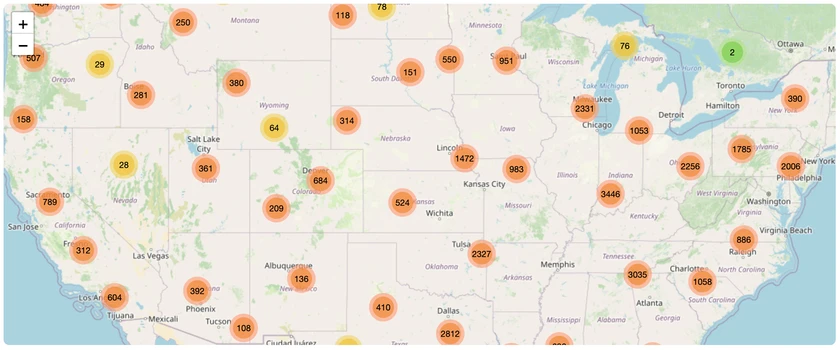 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
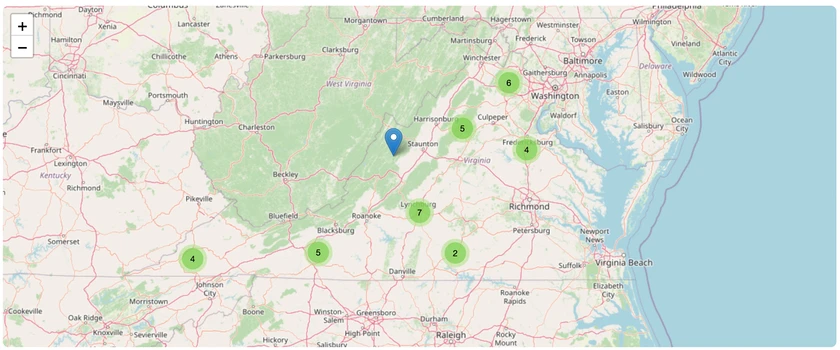 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
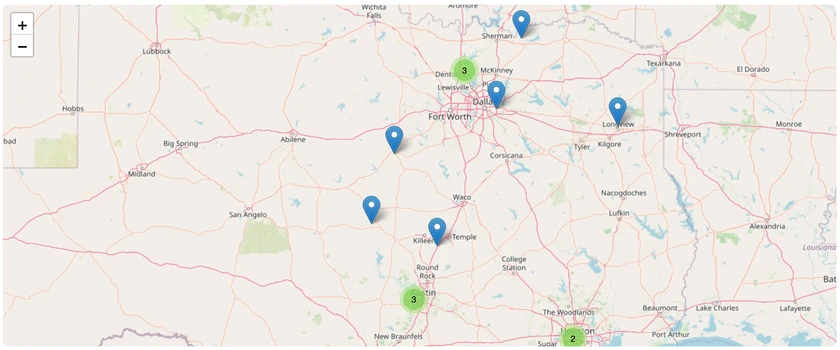 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












