Asian Black Bear
Ursus thibetanus
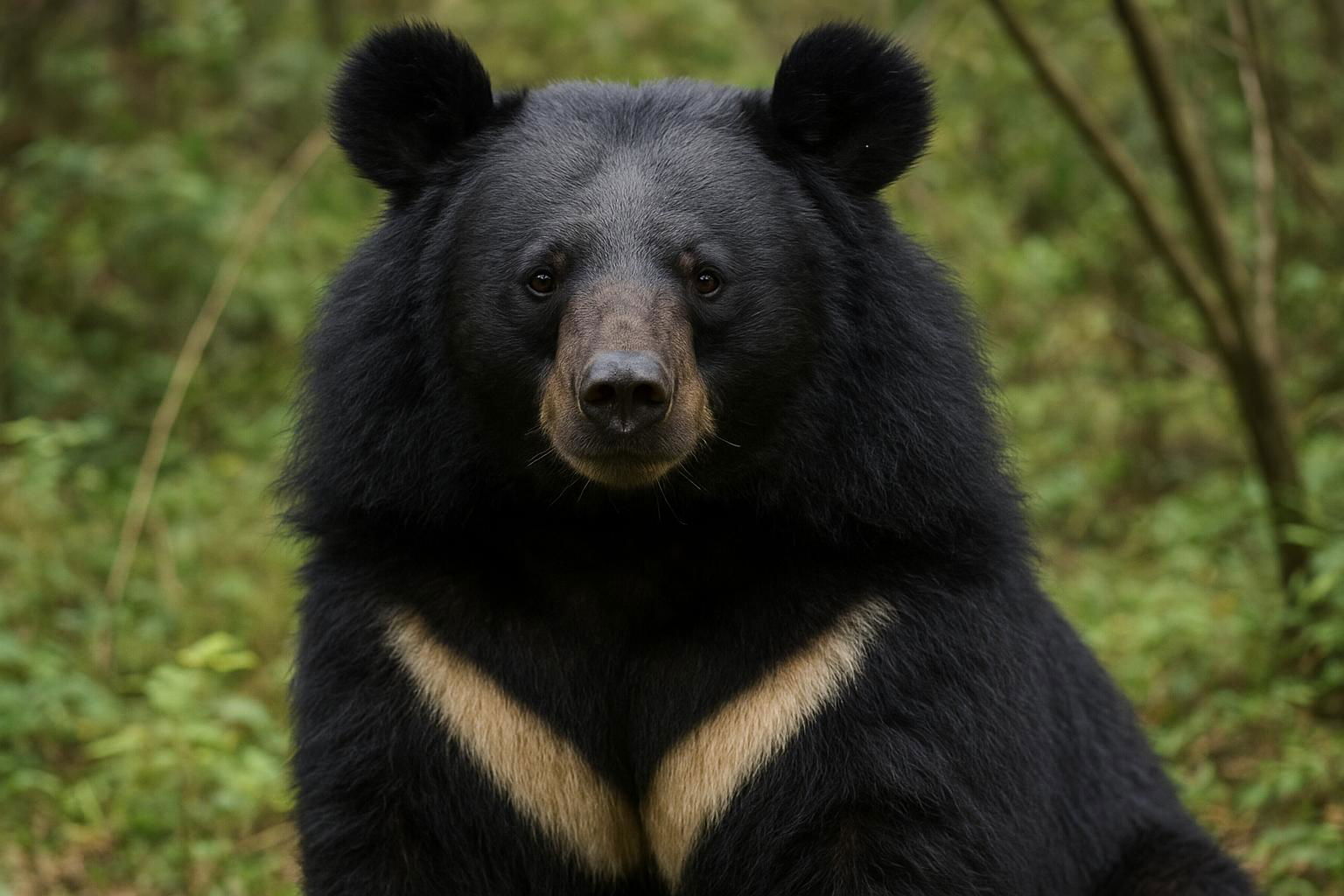
The Asian Black Bear, scientifically known as Ursus thibetanus, is a medium-sized bear species native to the forested areas of Asia, including the Himalayas, Southeast Asia, and parts of the Russian Far East. Characterized by its black fur and distinctive white chest patch, often resembling a crescent moon, these bears are also known as "moon bears." Adult males typically weigh between 90-200 kg (198-440 lbs), while females are slightly smaller. They possess strong, curved claws adapted for climbing, making them adept tree climbers in pursuit of food or safety.
Primarily nocturnal, the Asian Black Bear is an omnivore with a diet that includes a wide range of foods such as fruits, nuts, insects, small mammals, and carrion. In the wild, they play a crucial ecological role in seed dispersal and maintaining the health of their forest habitats. Socially, these bears are relatively solitary but communicate through vocalizations, scent markings, and physical gestures. While they adapt well to various environments, including subtropical and temperate forests, the species faces threats from habitat loss and poaching. Consequently, the Asian Black Bear is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, warranting ongoing conservation efforts to protect its remaining populations and natural environments.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
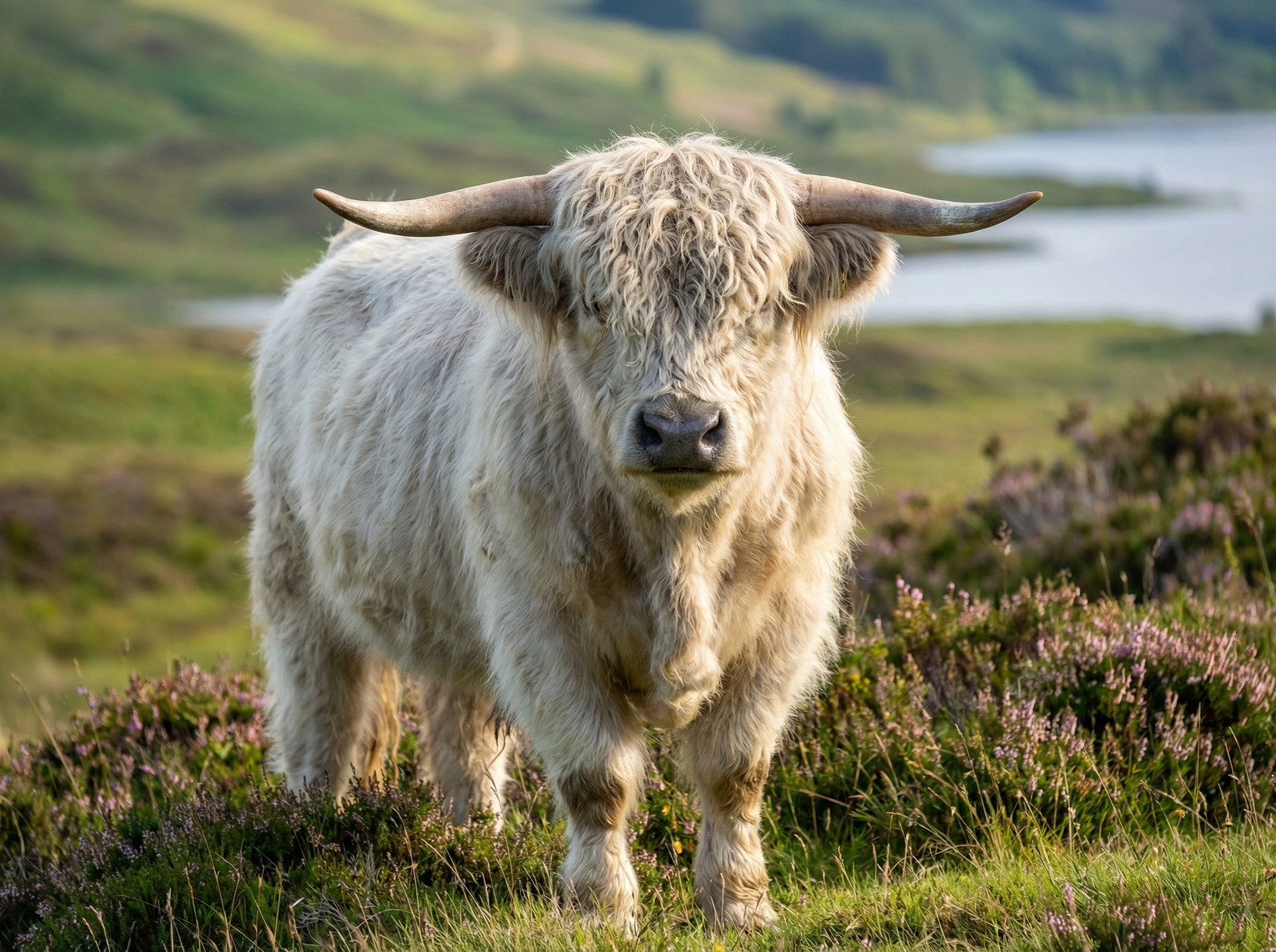 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
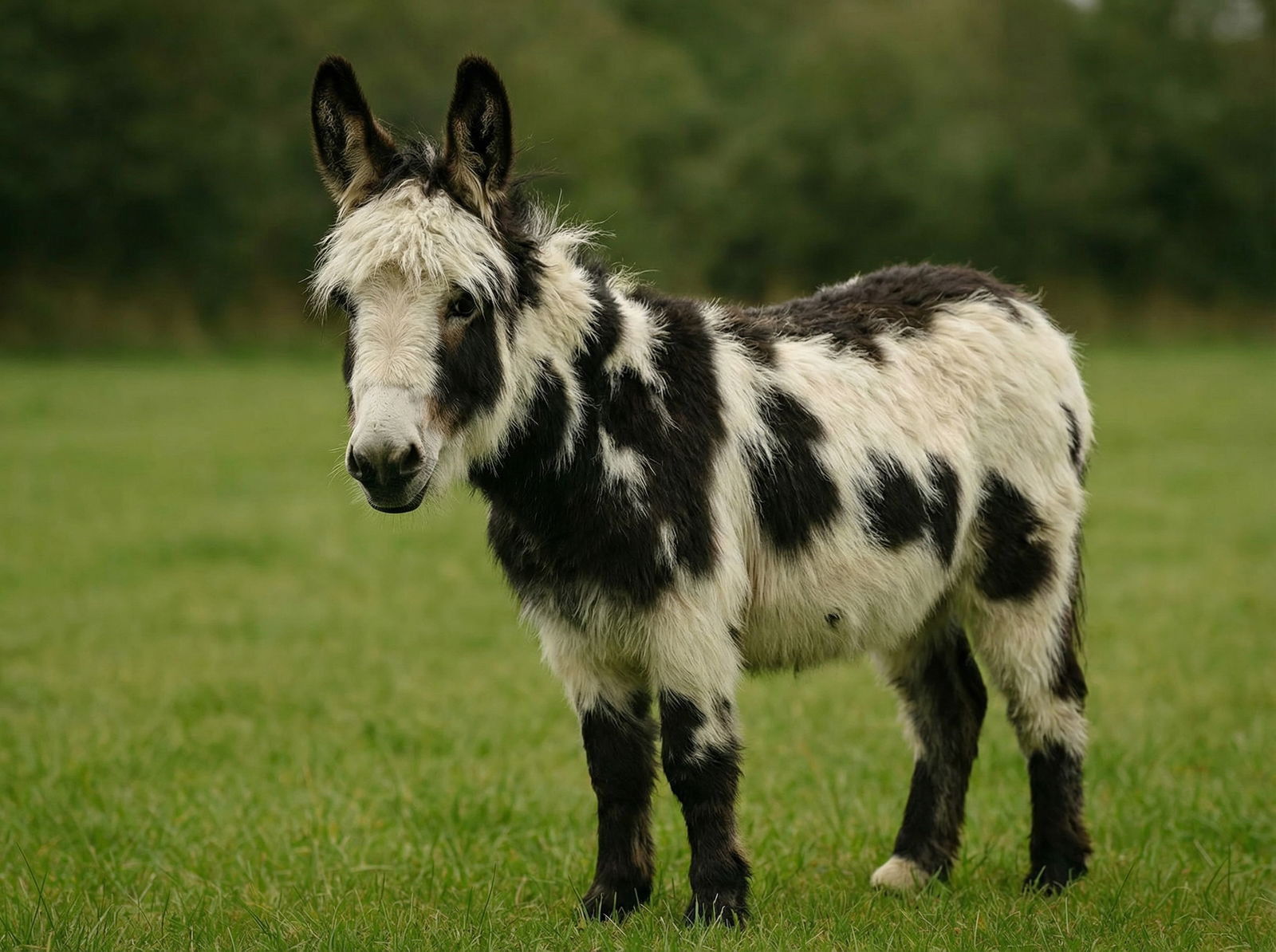 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
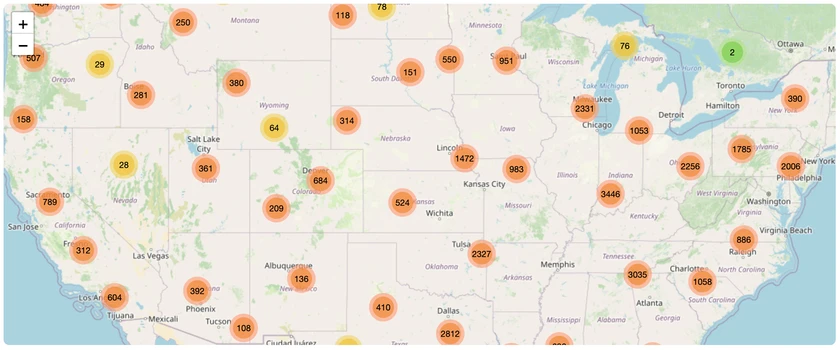 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
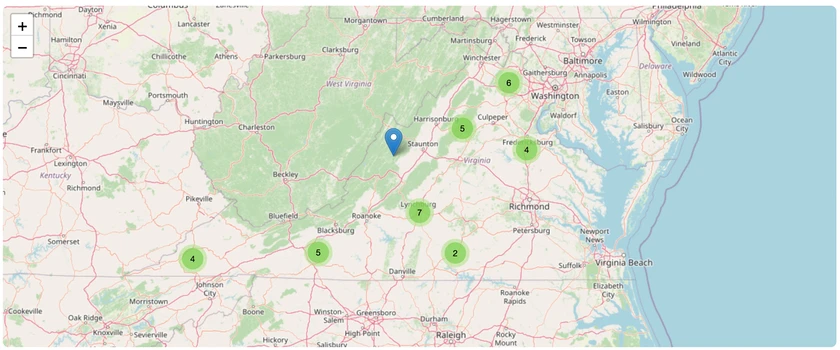 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
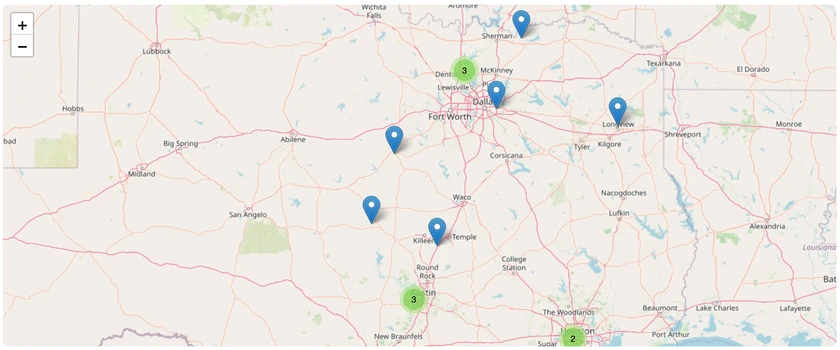 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












