African Wild Dog
Lycaon pictus
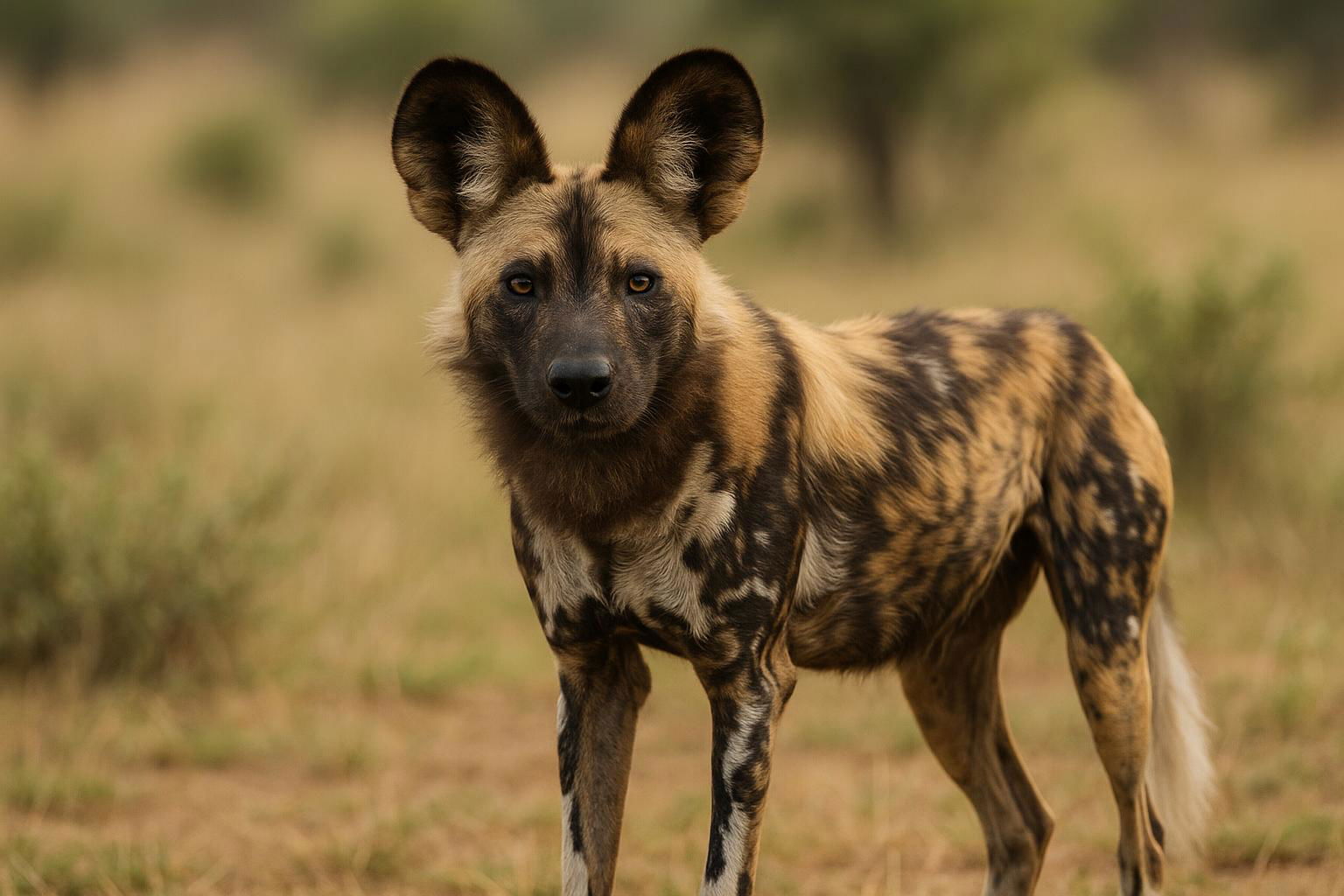
The African Wild Dog (Lycaon pictus), also known as the painted wolf or Cape hunting dog, is a distinctive and highly social carnivore native to the savannas, grasslands, and open woodlands of sub-Saharan Africa. Renowned for their striking multicolored coat, these canids display an intricate pattern of black, yellow, white, and brown patches, which are unique to each individual and serve as a natural form of identification. Adults typically weigh between 18 to 36 kilograms (40 to 79 pounds) and stand about 60 to 75 centimeters (24 to 30 inches) at the shoulder. Unlike other members of the Canidae family, African Wild Dogs possess only four toes per foot, rather than the typical five.
These animals are highly social and live in packs of about 6 to 20 individuals, led by an alpha pair. The pack operates with an intricate social structure, emphasizing cooperation in hunting and rearing young. They are renowned for their hunting efficiency, boasting a success rate of around 80%, thanks to their ability to communicate and strategize during their coordinated pursuit of prey, which primarily includes antelopes. African Wild Dogs are known for their stamina and can cover large distances during hunts. Sadly, these magnificent animals are classified as endangered due to habitat fragmentation, human-wildlife conflict, and susceptibility to diseases like rabies and distemper. Conservation efforts are concentrated on preserving their habitats and ensuring genetic diversity across populations to support the survival of this unique species.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
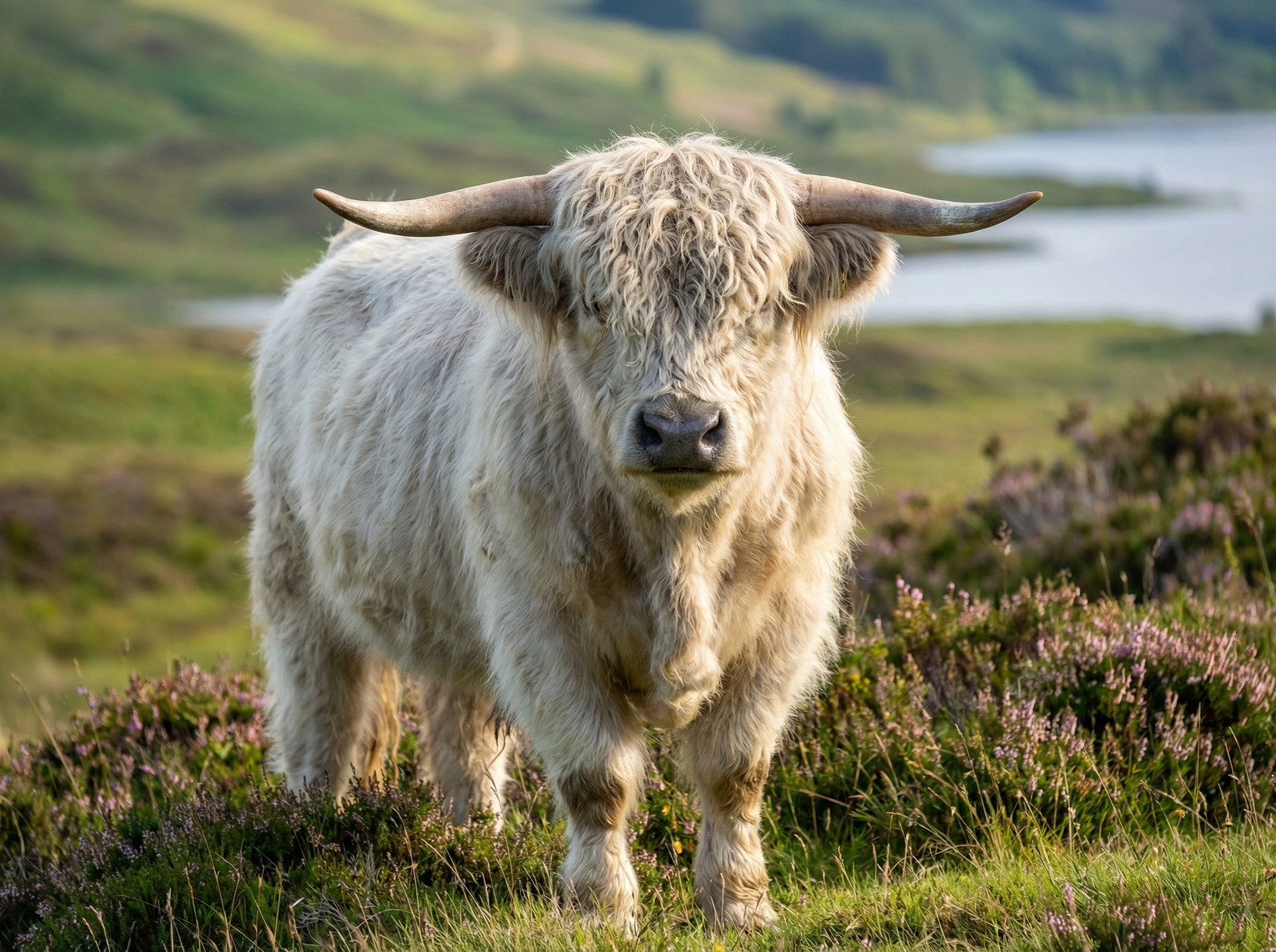 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
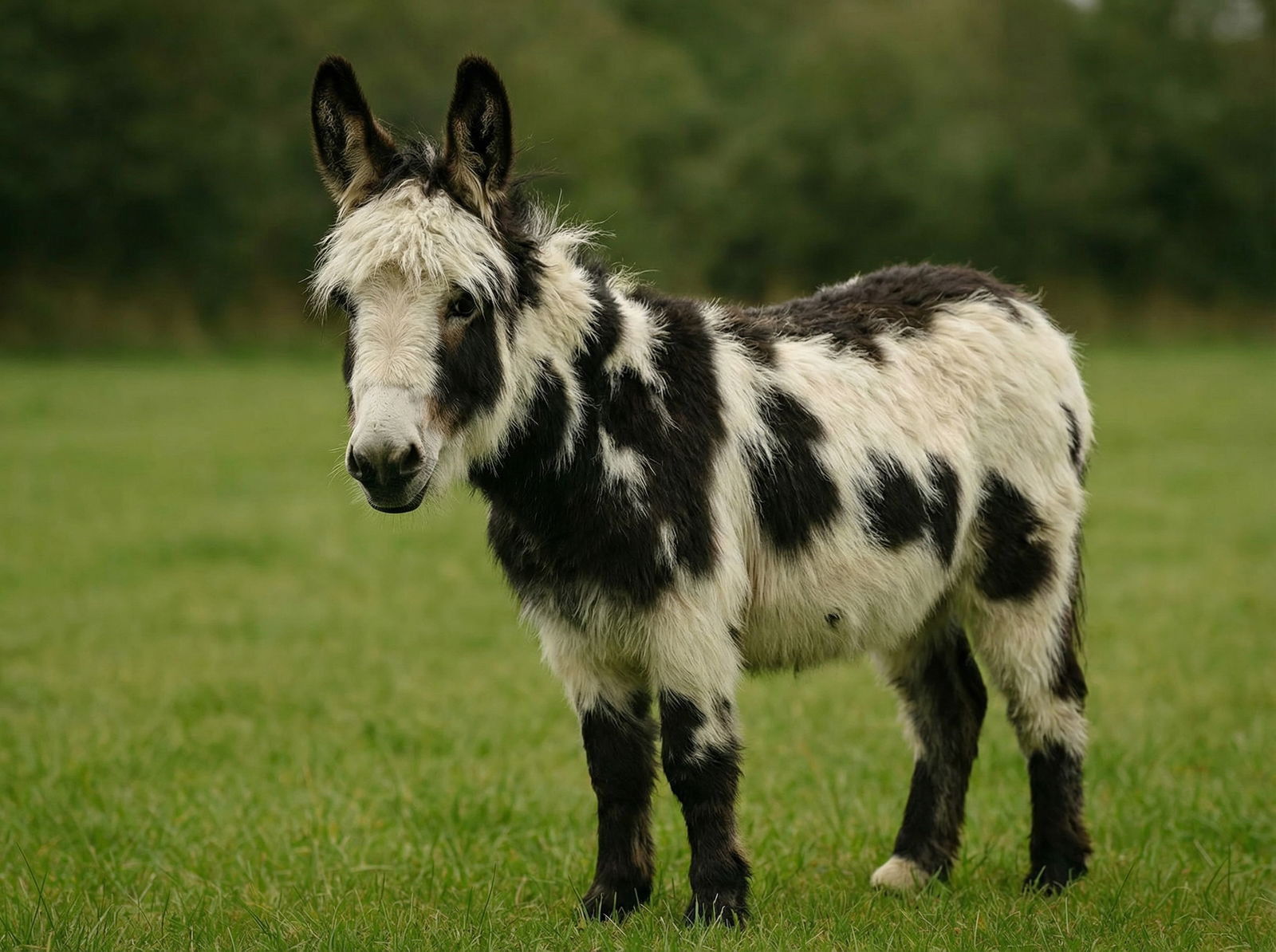 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
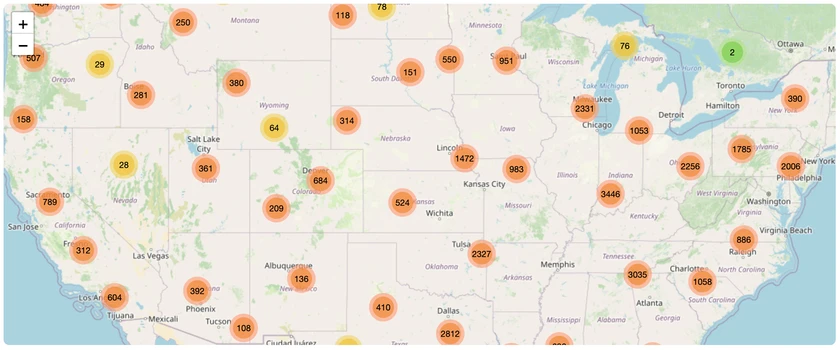 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
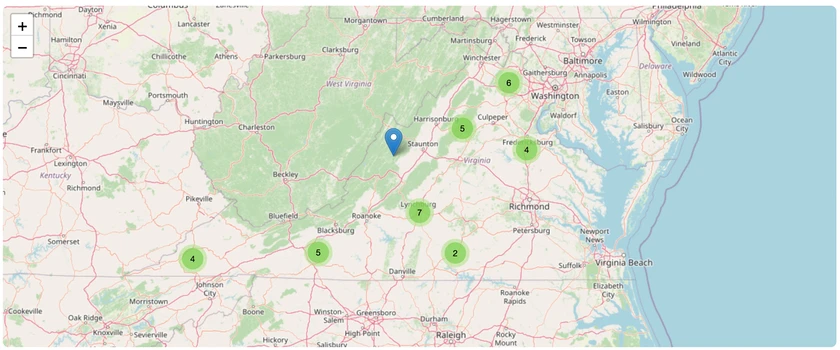 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
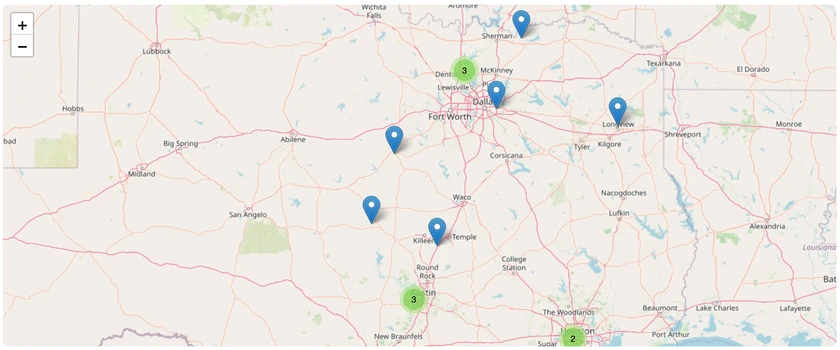 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












