Addax
Addax nasomaculatus
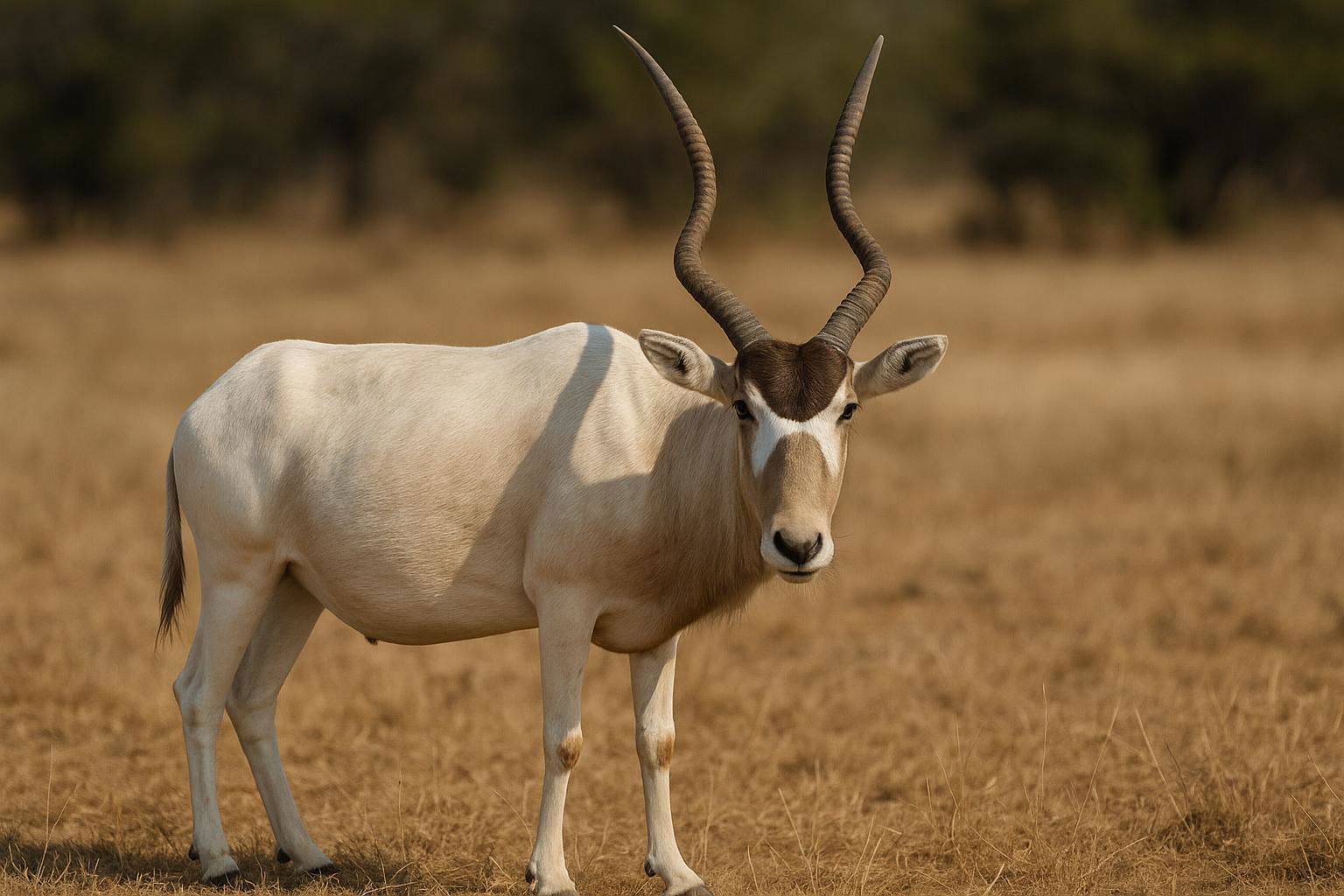
The addax (Addax nasomaculatus), also known as the white antelope or screwhorn antelope, is a critically endangered species native to the Sahara Desert in Northern Africa. This elegant antelope is perfectly adapted to its harsh, arid environment. It has a striking appearance, featuring a predominantly white or light-colored coat that reflects sunlight, helping to keep it cool, with longer tufts of hair around the neck during the cold winter months. The addax is most distinctive for its twisted, spiral horns that can reach up to 3 feet in length, sported by both males and females. These horns are used for defense and in dominance duels among males.
Physically built for desert life, the addax has wide hooves with flat soles that prevent sinking into the sand. It is a highly nomadic grazer, feeding primarily on grasses, leaves, and shrubs, and can survive without direct water sources, obtaining moisture from its food. Socially, addaxes live in small herds led by a dominant female, although solitary individuals are also common. The species' numbers have drastically dwindled due to over-hunting and habitat loss, leading to their current status on the IUCN Red List. Conservation efforts are ongoing, focusing on habitat protection and reintroduction programs to stabilize and eventually increase addax populations in the wild.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
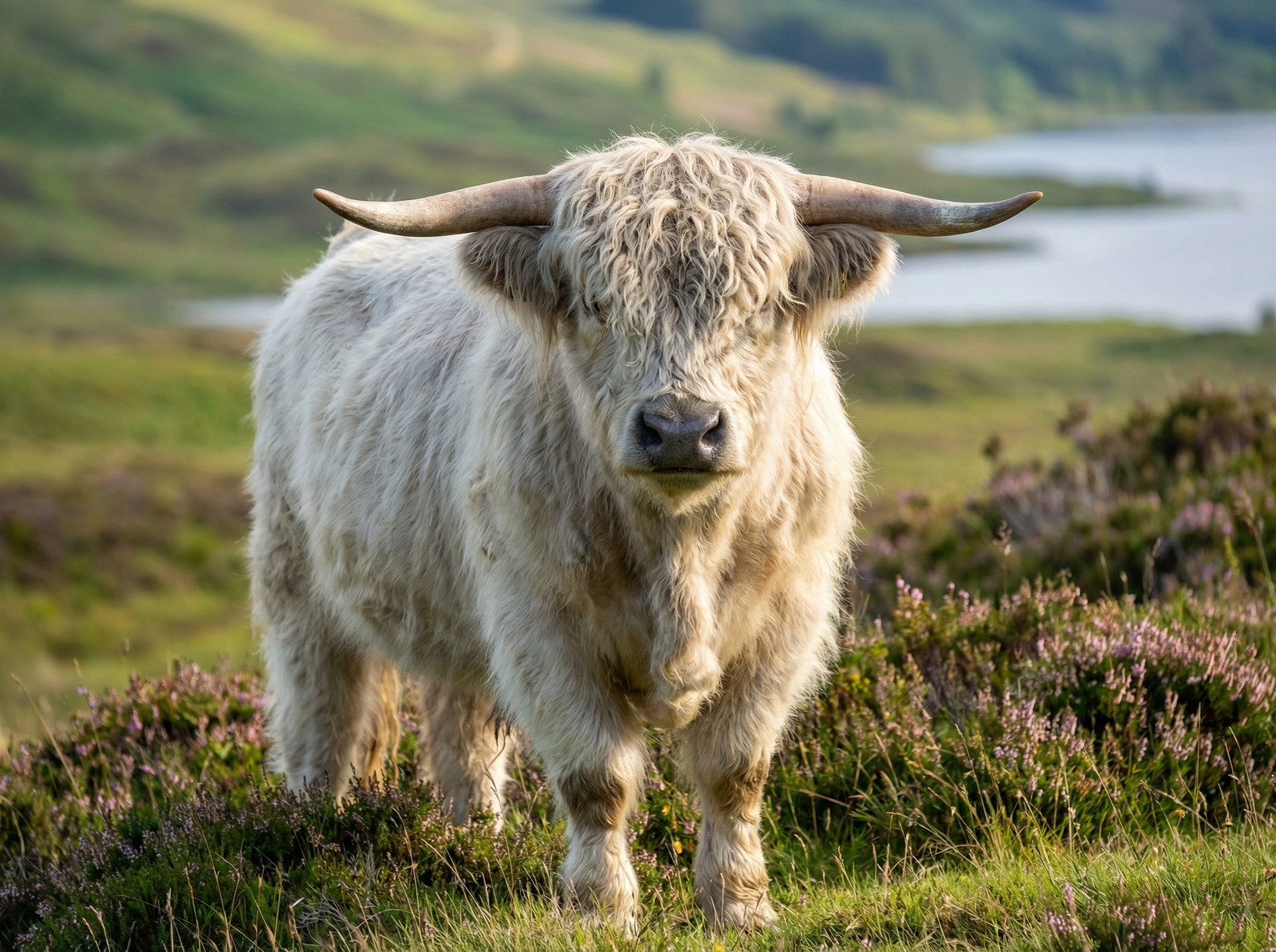 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
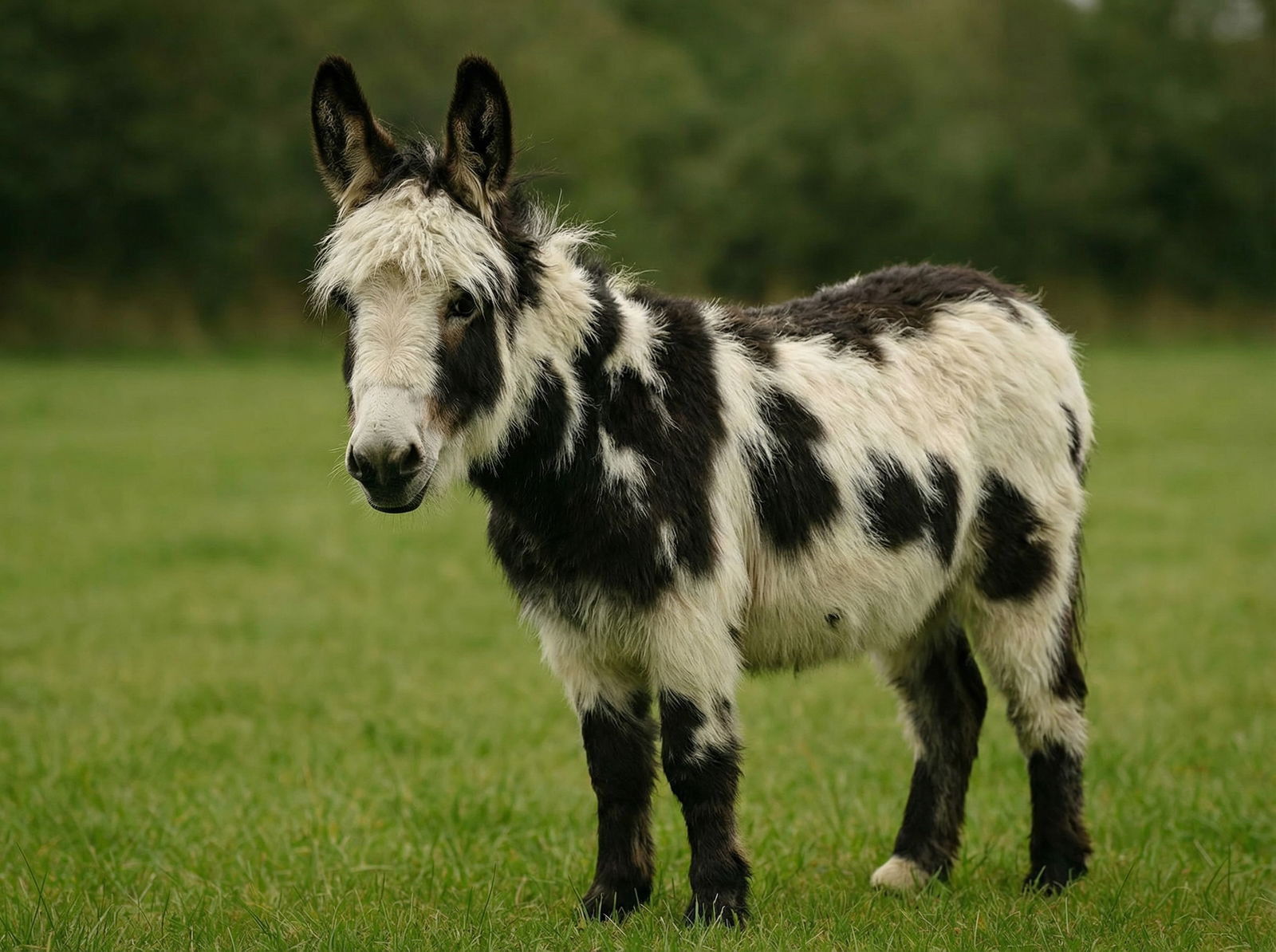 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












