White-Handed Gibbon
Hylobates lar
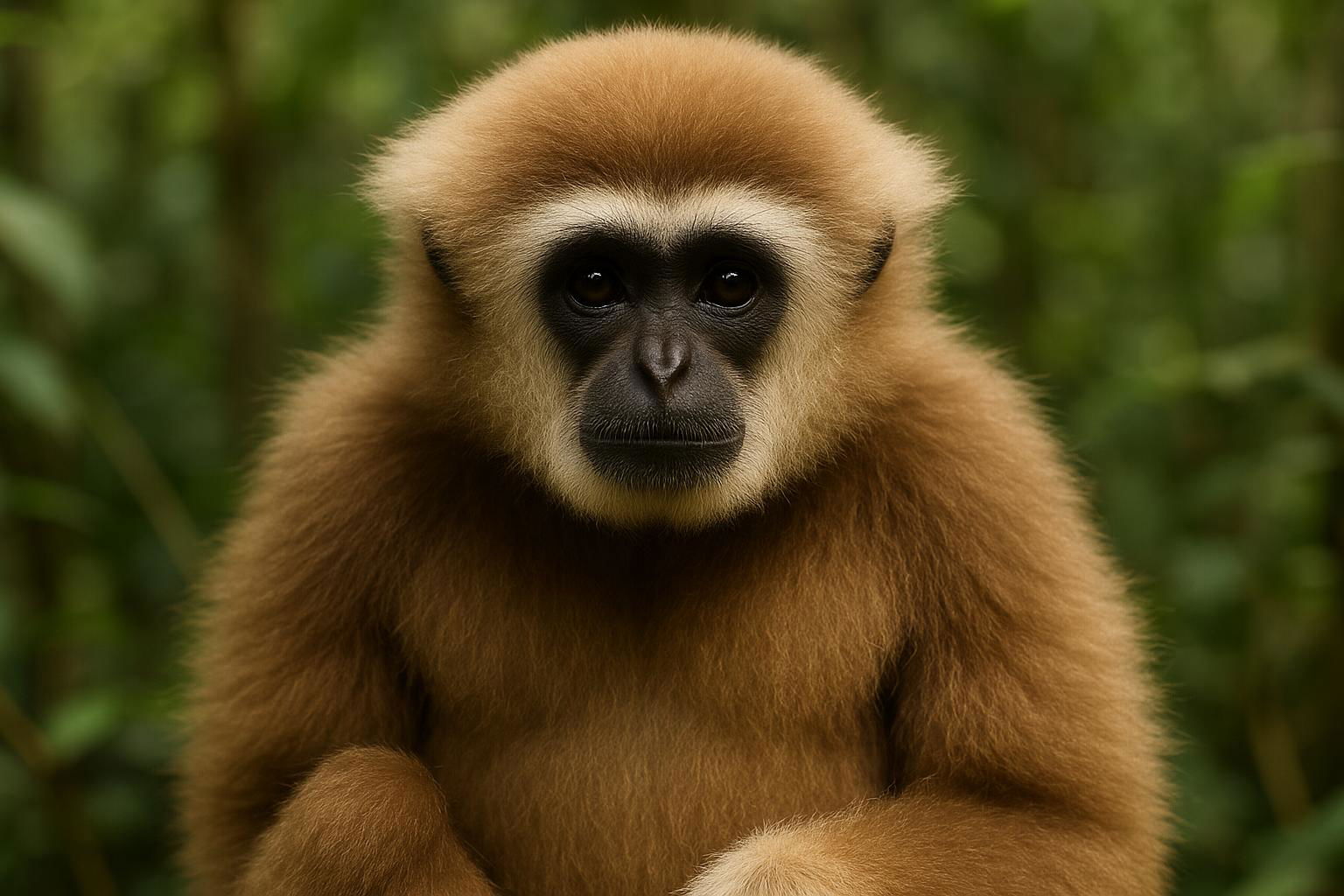
The White-Handed Gibbon, scientifically known as Hylobates lar, is a captivating and agile primate native to the dense tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia, particularly found in countries like Thailand, Malaysia, and Sumatra. These gibbons are renowned for their remarkable brachiation abilities, swinging gracefully between branches using their long arms, which are significantly longer than their legs. This small, diurnal ape is characterized by its thick, dense fur that ranges in color from cream to black, and as their name suggests, they have distinct white fur on their hands and feet, as well as a white facial ring encircling their dark-skinned face.
White-Handed Gibbons are highly social animals, typically living in small, monogamous family groups that exhibit strong pair bonds. Their communication repertoire includes a complex series of calls and songs, which serve to establish territory and strengthen family bonds. Vocal duets between mating pairs are especially notable, resonating through the forest in harmonious choruses.
These gibbons primarily feed on a diet of ripe fruits, leaves, and occasional insects, contributing to their role as essential seed dispersers within their ecosystem. Unfortunately, the White-Handed Gibbon faces threats from habitat destruction and hunting, leading to a decline in their population. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the survival of this enchanting species and the preservation of their natural habitat.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
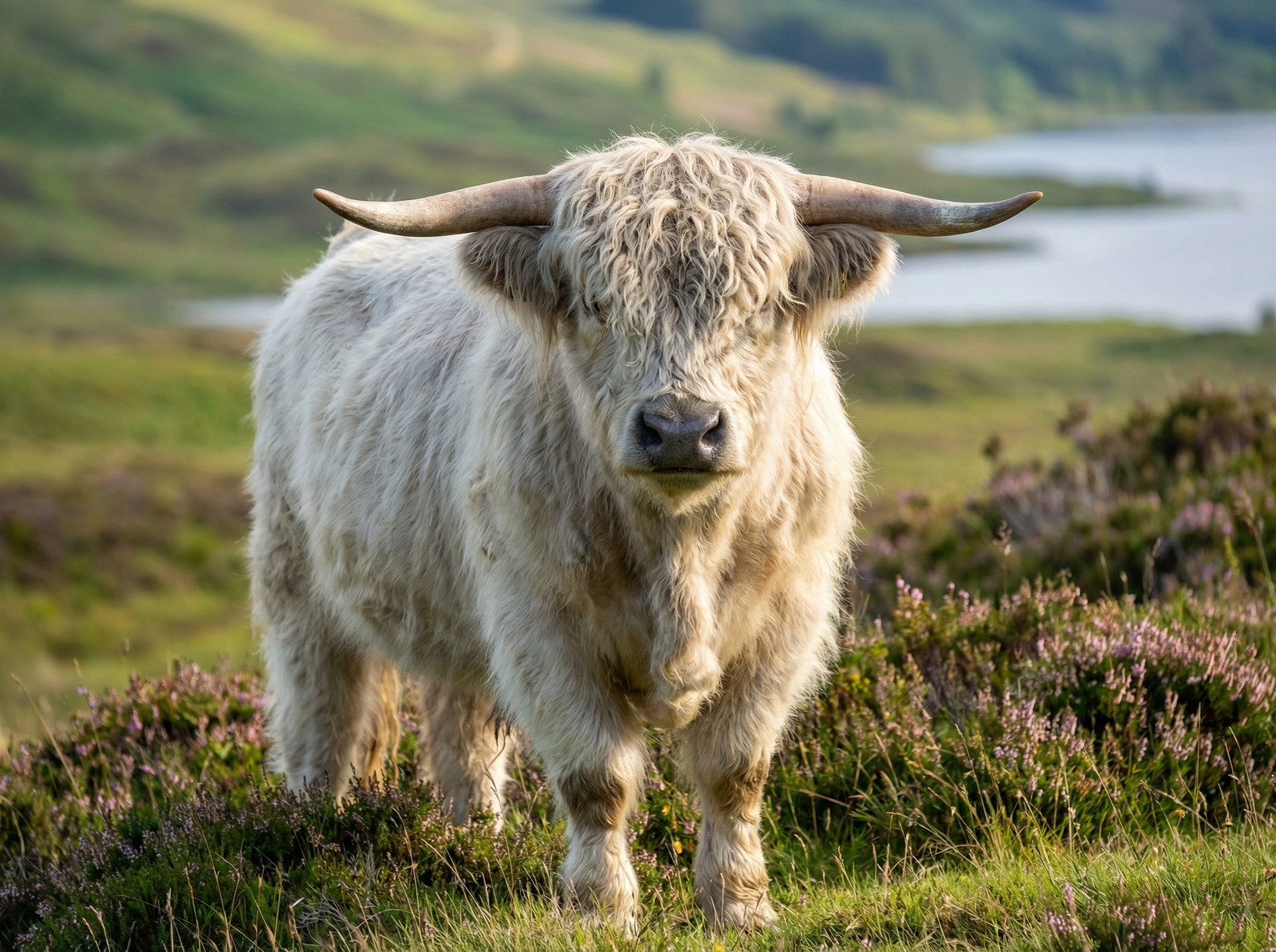 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
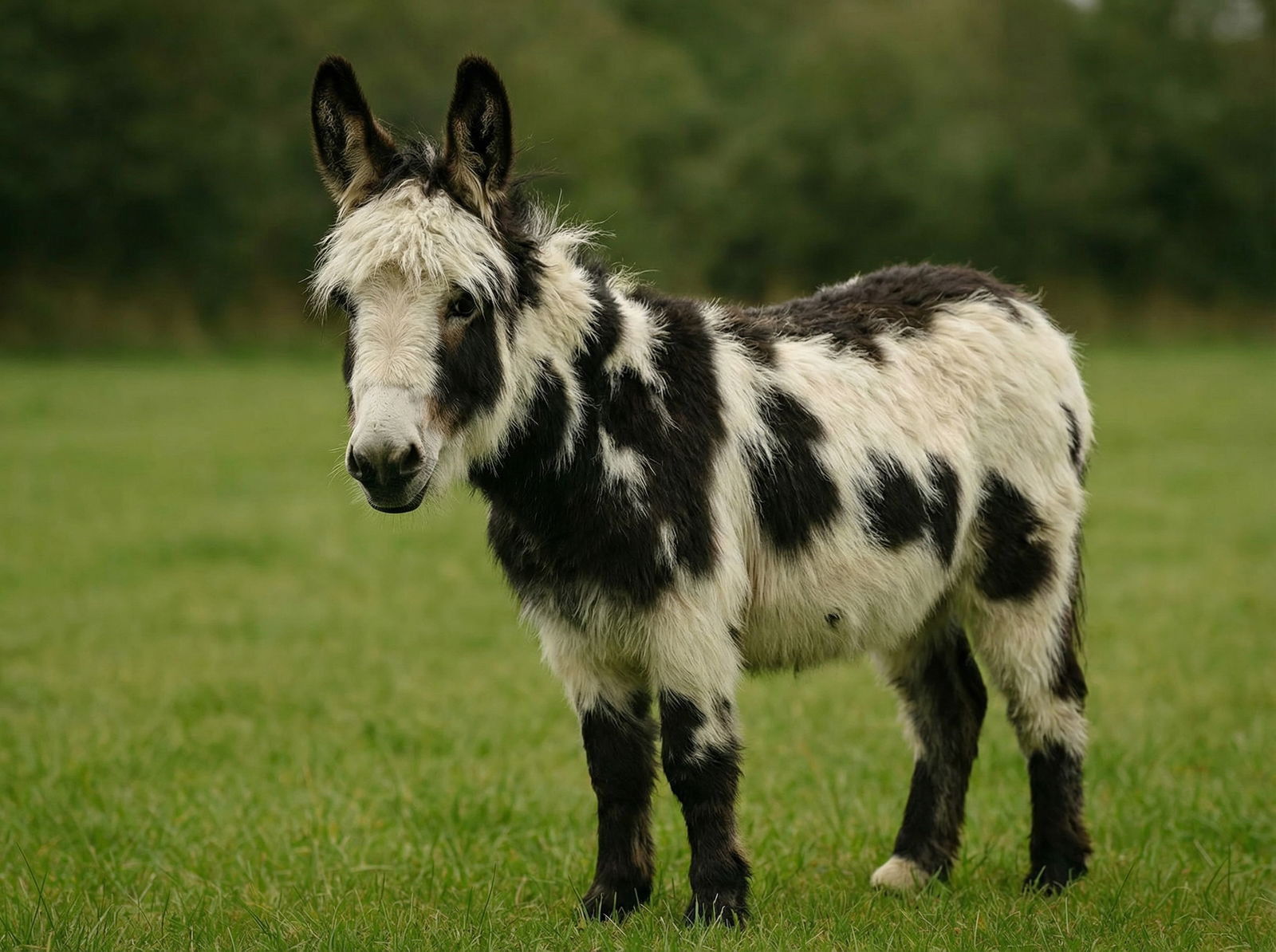 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












