Meerkat
Suricata suricatta
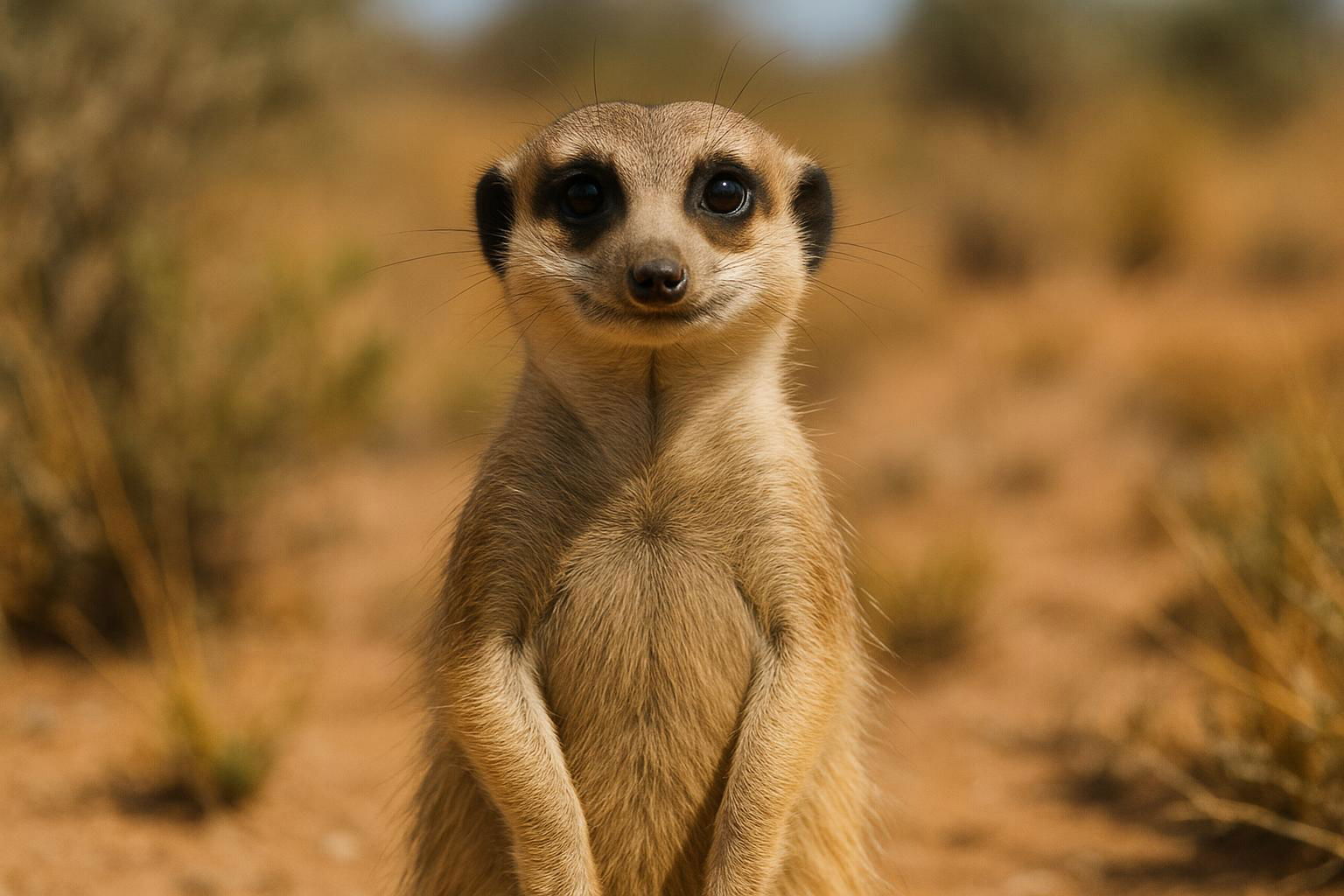
The meerkat (Suricata suricatta) is a small mammal belonging to the mongoose family, Herpestidae. Native to the arid regions of southern Africa, including the Kalahari Desert and parts of Namibia, Angola, and South Africa, meerkats are known for their highly social behavior and cooperative living structures. They typically inhabit open plains and sparsely wooded areas, where they rely on an intricate network of underground burrows for shelter. Distinctively, meerkats have slender bodies covered in light brown to grey fur with stripes on their backs, and their eyes are surrounded by dark patches that help reduce glare from the sun.
Meerkats are diurnal and spend much of their day foraging for food, which consists mainly of insects, but also includes small vertebrates, eggs, and plant matter. Their cooperative social structure is organized into groups known as "mobs," "gangs," or "clans," which can consist of up to 30 individuals. Within these groups, meerkats display strong kin-based cooperation, taking turns as sentinels to watch for predators while others forage. They communicate through a complex system of vocalizations to convey alerts and coordinate activities. Meerkats have adapted an impressive ability to stand upright on their hind legs, using their tails for balance, to gain a better vantage point for spotting threats. Their intricate social behaviors, adaptability, and engaging personality have made meerkats a popular subject of study in behavioral ecology and a beloved animal in popular culture.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
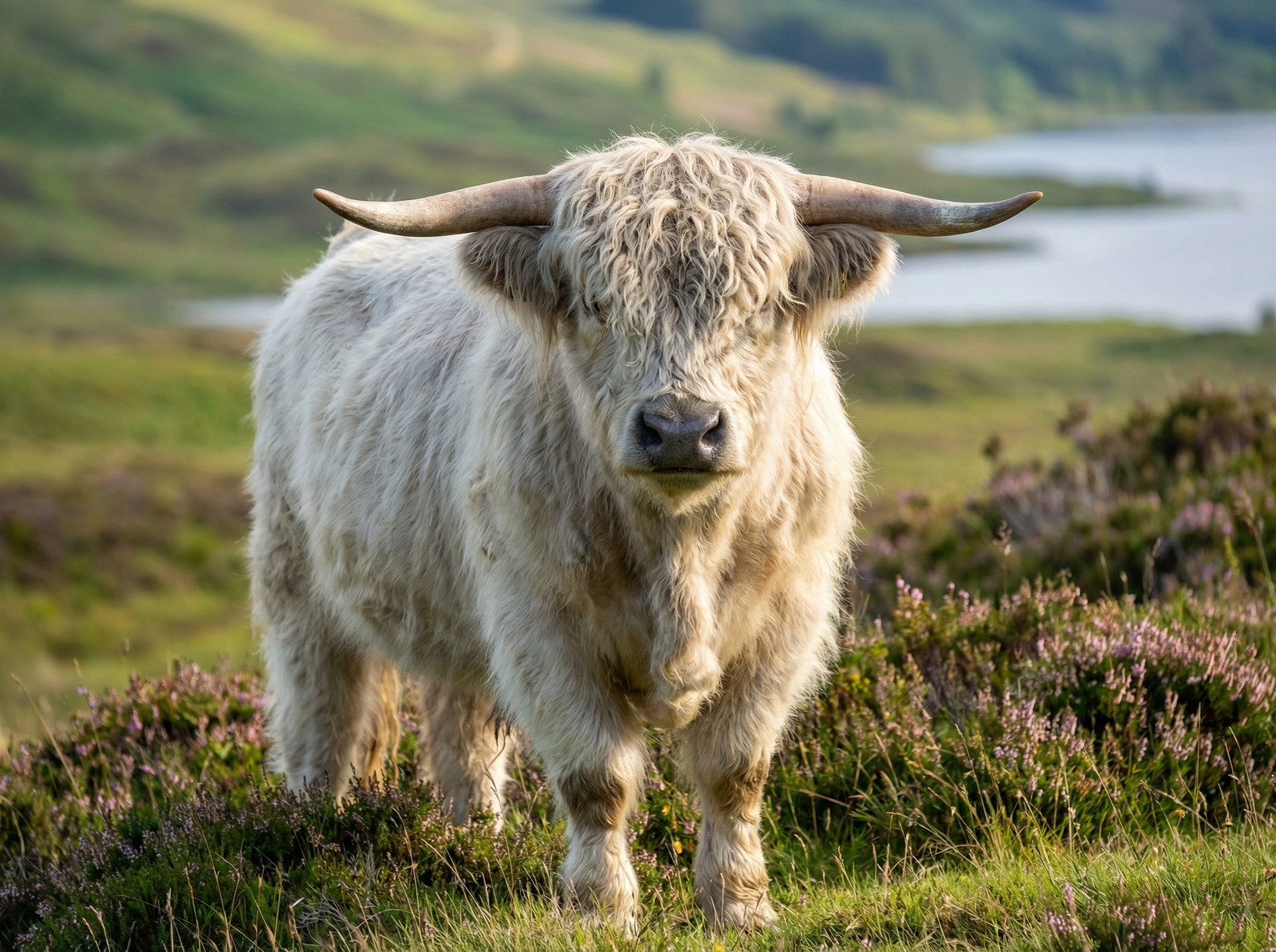 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
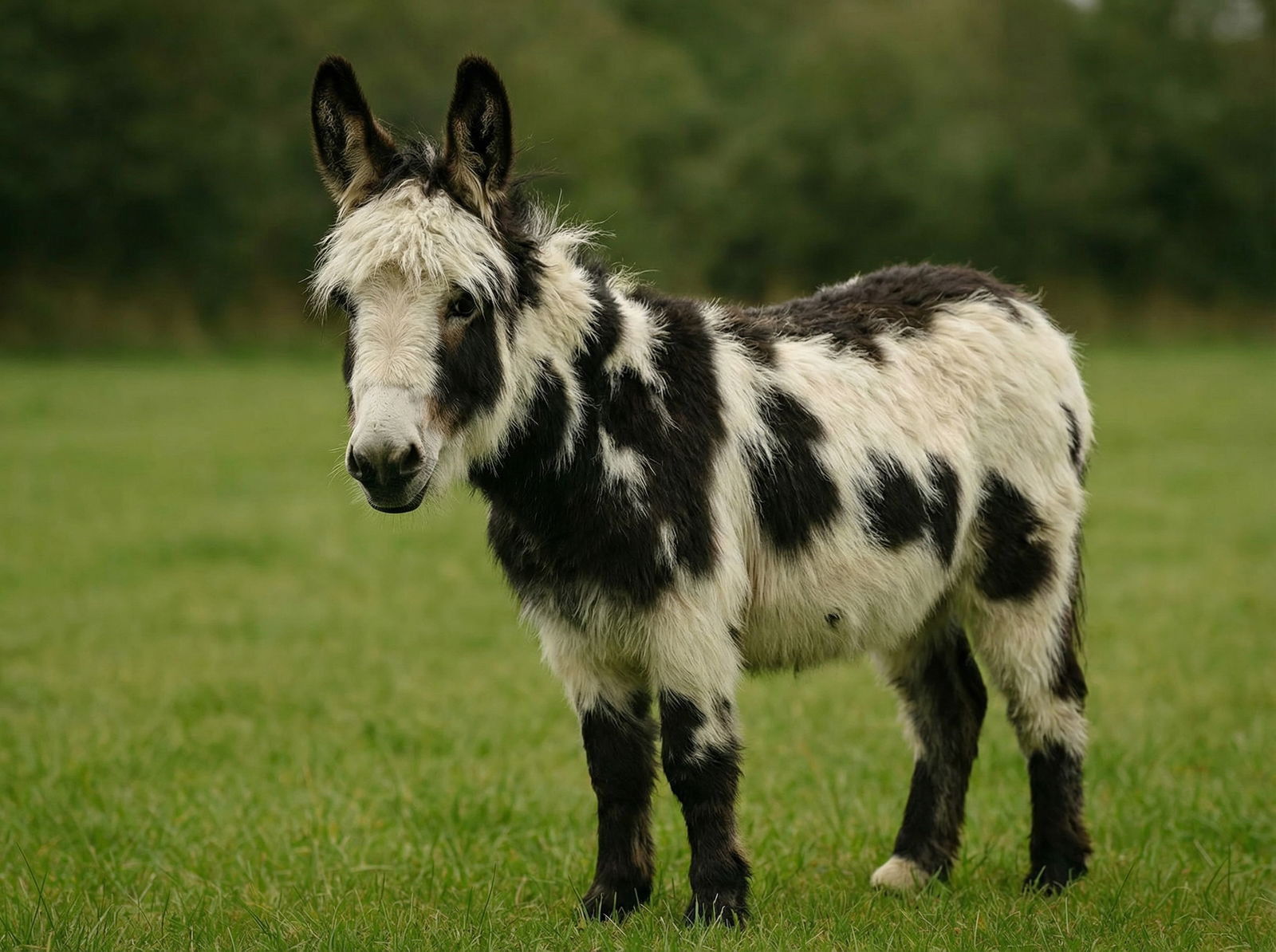 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
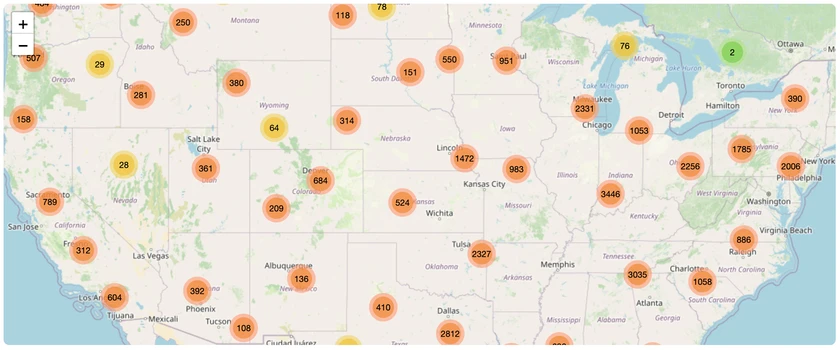 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
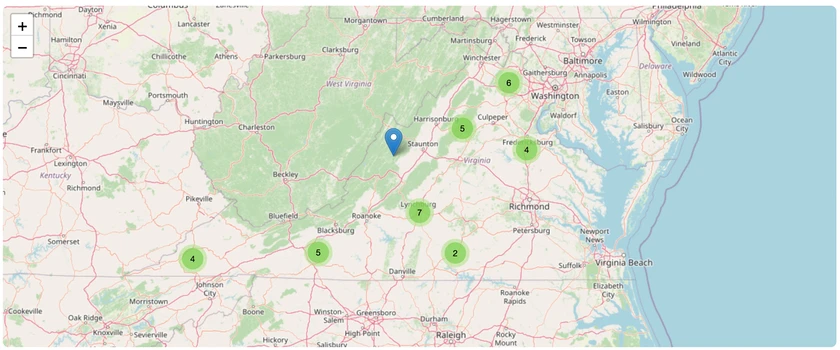 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
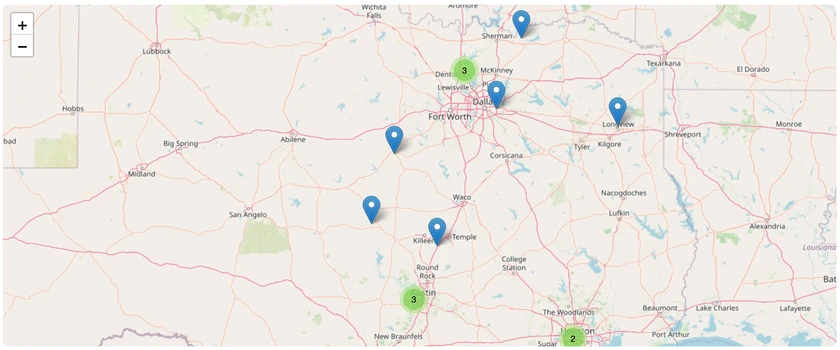 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












