Galapagos Giant Tortoise
Chelonoidis niger
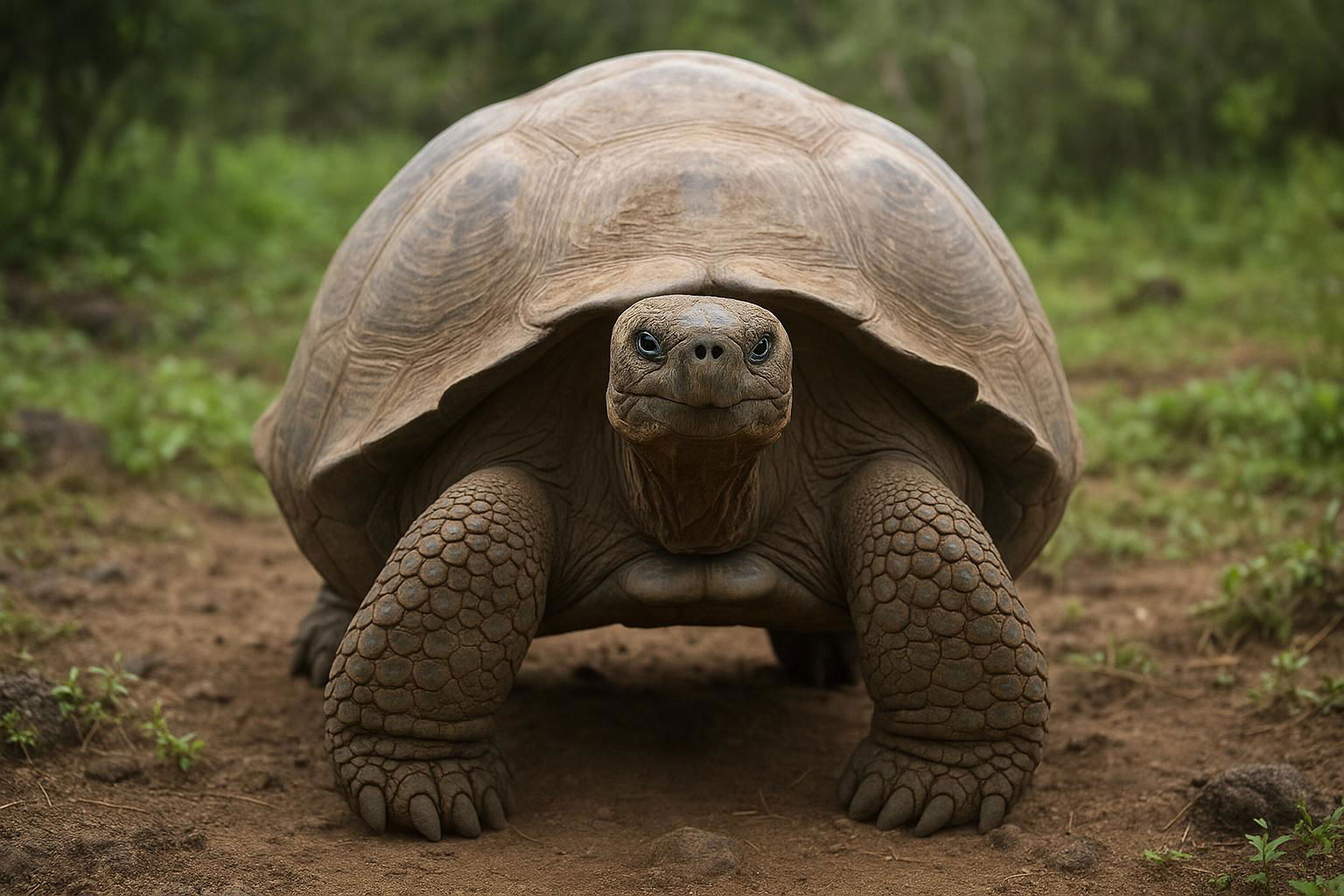
The Galápagos Giant Tortoise, scientifically known as Chelonoidis niger, is an iconic reptile species native to the Galápagos Islands. Renowned for its impressive size, it is one of the largest tortoise species in the world, with some individuals weighing over 900 pounds and measuring up to 5 feet in length. These tortoises have domed shells and sturdy limbs, suited for life in diverse island habitats ranging from lush highland forests to arid lowlands. Notably, they can live well over 100 years, making them one of the longest-lived vertebrates.
Galápagos Giant Tortoises are primarily herbivorous, feeding on a variety of grasses, leaves, and fruits. Their slow metabolism and ability to store water allow them to endure long periods without food or water, an adaptation crucial for survival on islands with fluctuating resources. Socially, they can often be seen basking in the sun, wallowing in mud, or slowly traversing their environment.
Conservation efforts are crucial for Chelonoidis niger, as their populations have been historically threatened by human activities such as hunting and habitat destruction, as well as by introduced species. Today, conservation programs aim to restore their habitat and maintain genetic diversity, ensuring the survival of this magnificent species, which continues to captivate and inspire curiosity around the world.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
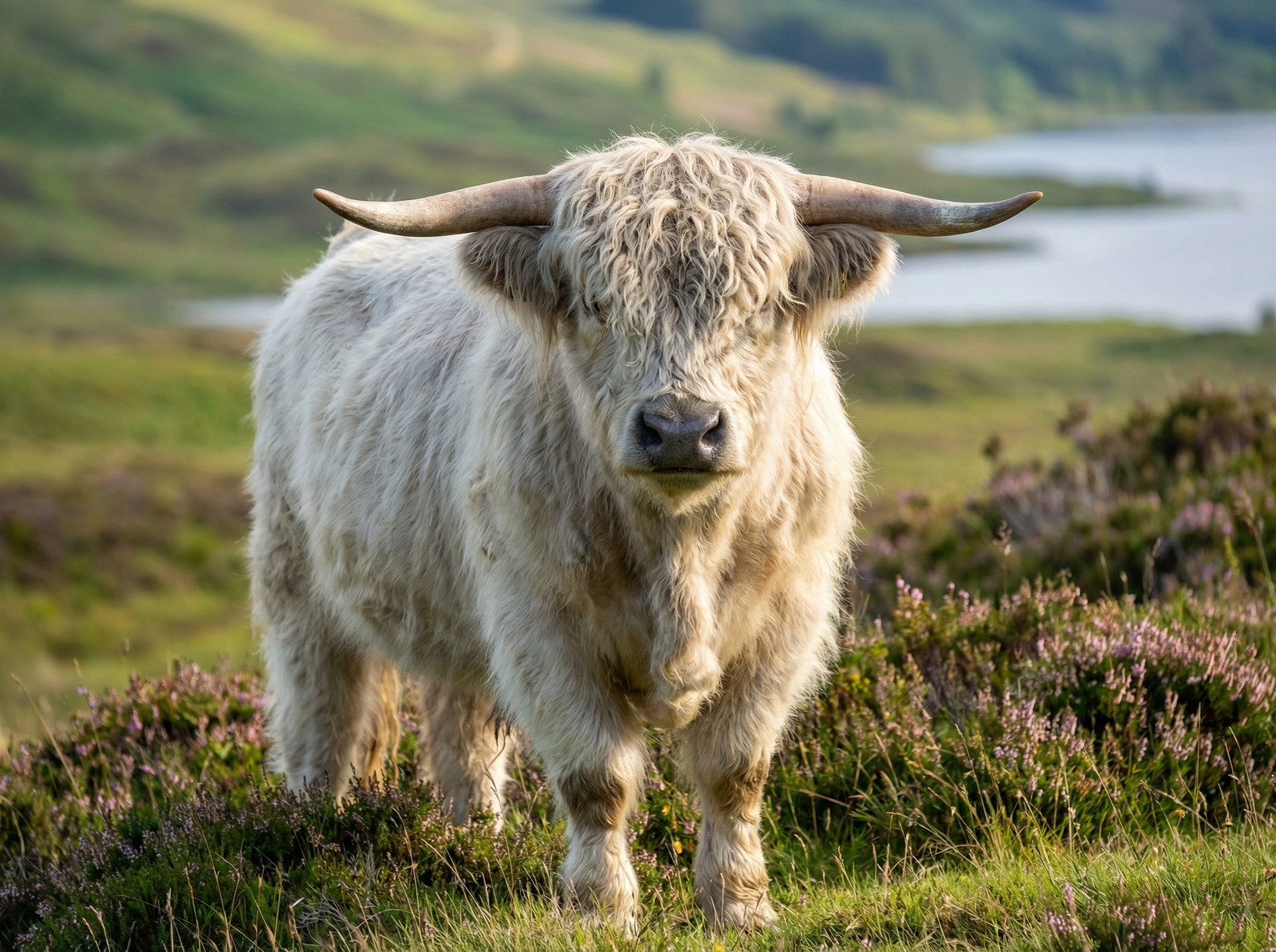 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
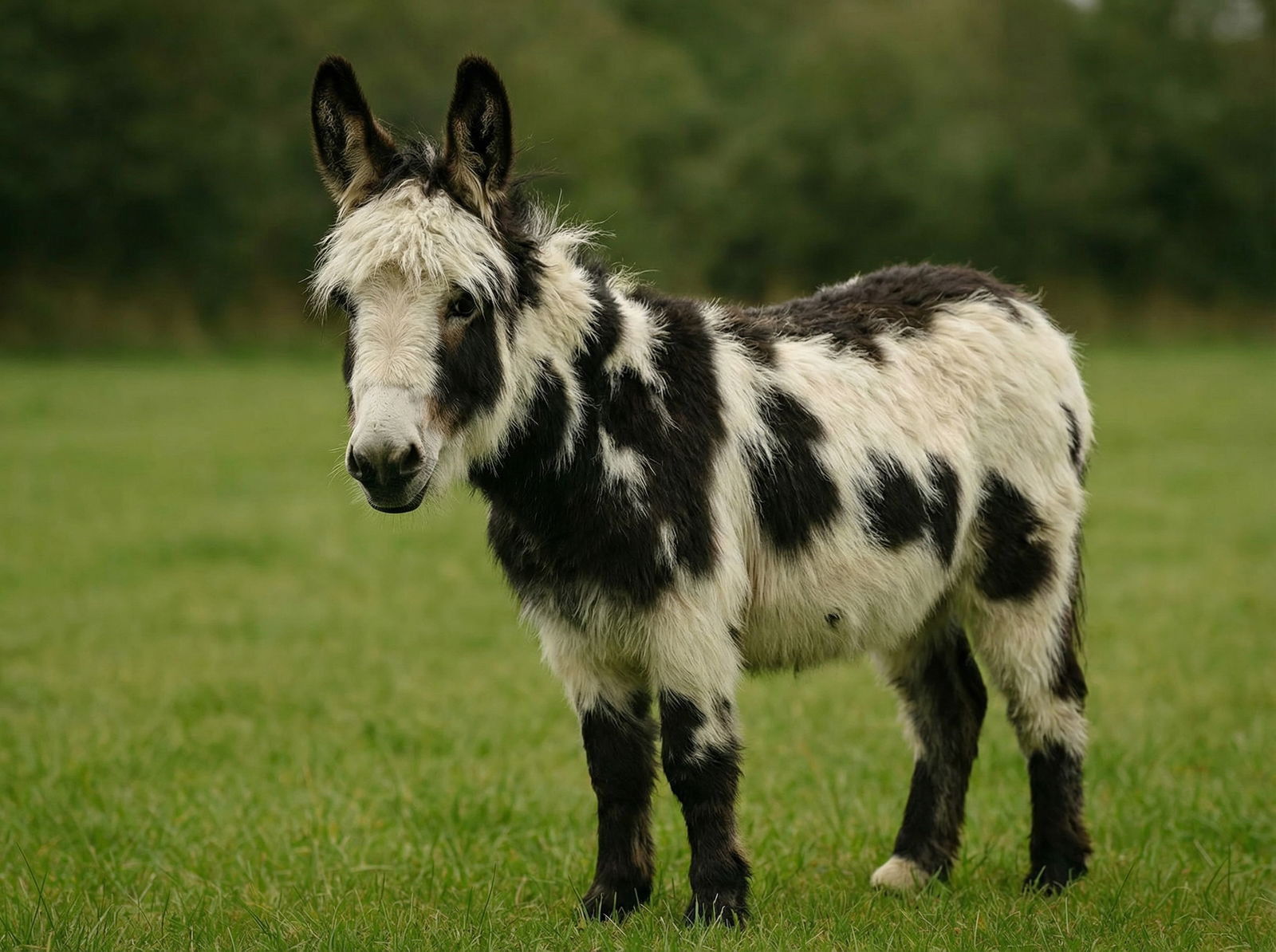 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
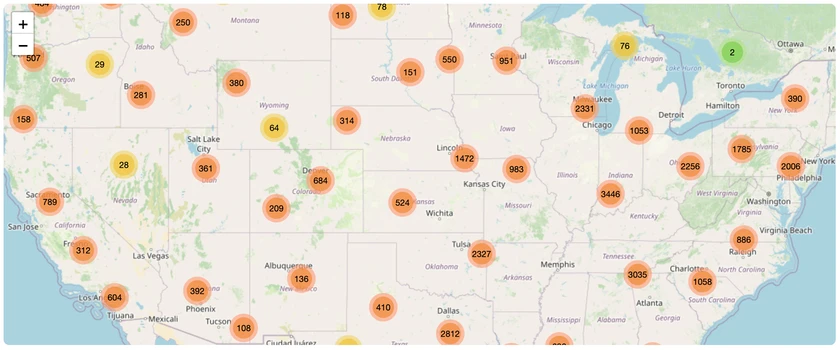 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
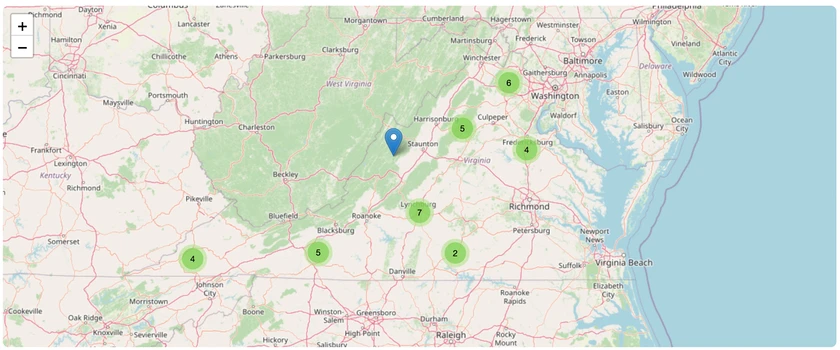 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
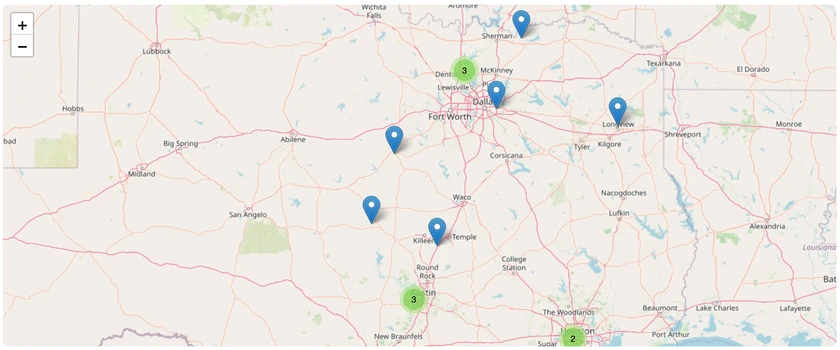 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












