Arizona Blonde Tarantula
Aphonopelma chalcodes
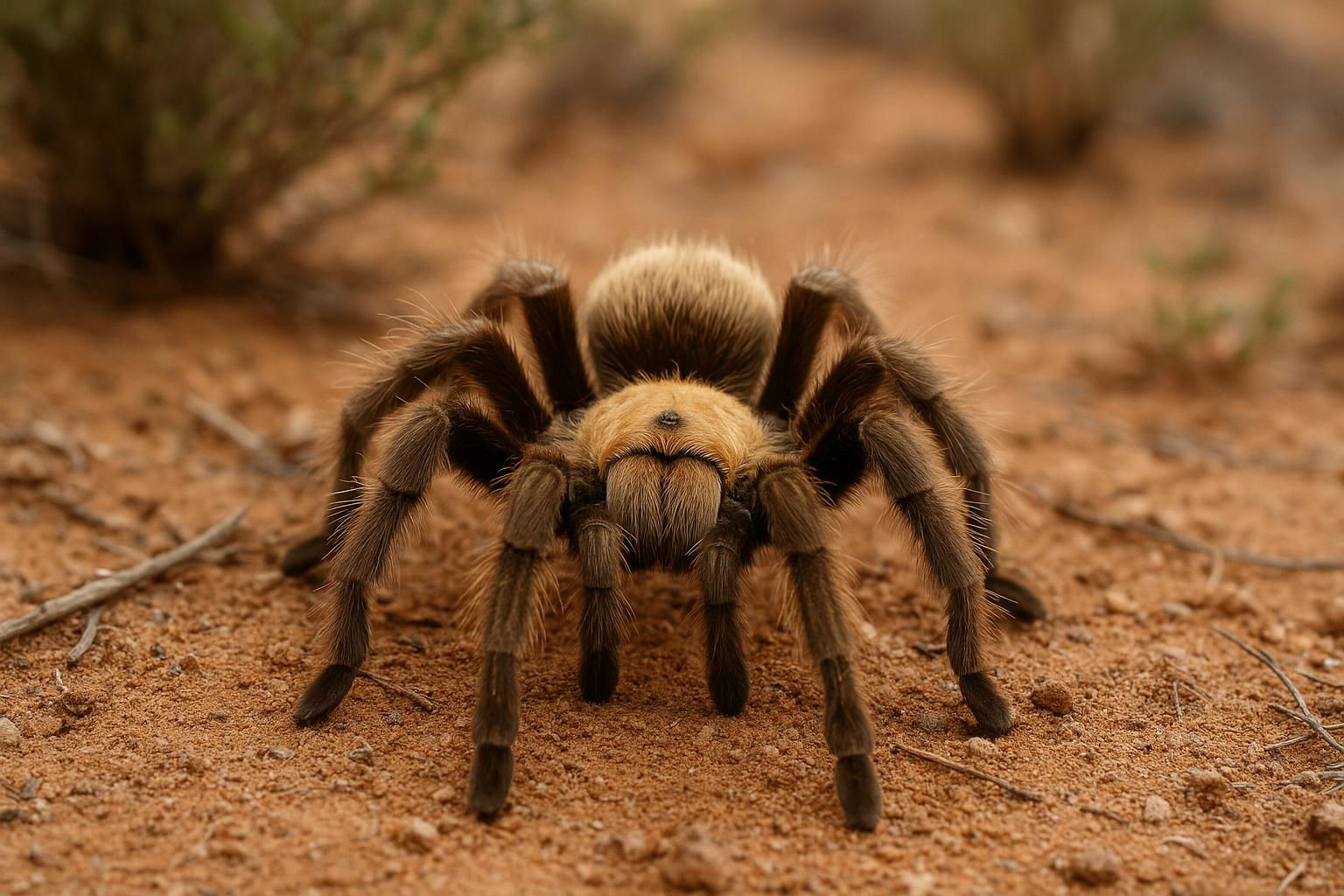
The Arizona Blonde Tarantula, scientifically known as Aphonopelma chalcodes, is a captivating species native to the desert regions of the southwestern United States, especially prevalent in Arizona. It is easily recognized by its striking appearance, characterized by a distinct coloration pattern that gives it its common name. The females generally exhibit a pale, sandy blond carapace and ivory-hued legs, contrasting with a darker brown abdomen, while males often display more uniform and darker tones.
This species, like other tarantulas, is terrestrial and fossorial, meaning it spends much of its life in burrows that it excavates in the desert soil. These burrows provide protection from both predators and the extreme temperatures of their arid habitat. The Arizona Blonde Tarantula is a relatively large and robust spider, with females reaching up to 3 inches in body length and sporting a leg span of around 6 inches. Males are typically smaller and more slender.
These tarantulas are predominantly nocturnal hunters, preying on a diet of insects and other small invertebrates. Despite their formidable size and intimidating appearance, Arizona Blonde Tarantulas are known for their docile nature, making them a popular choice among tarantula enthusiasts and collectors. They also have a long lifespan, with females living up to 20-25 years in captivity, while males generally live for about 5-10 years.
During the breeding season, males venture from their burrows in search of females. After mating, females lay eggs in silk-lined sacs, which they guard fiercely. The Arizona Blonde Tarantula plays a vital role in its ecosystem, helping to control insect populations and serving as prey for larger animals. Their presence is a testament to the delicate balance of life in the desert.

 All Species & Breeds
All Species & Breeds
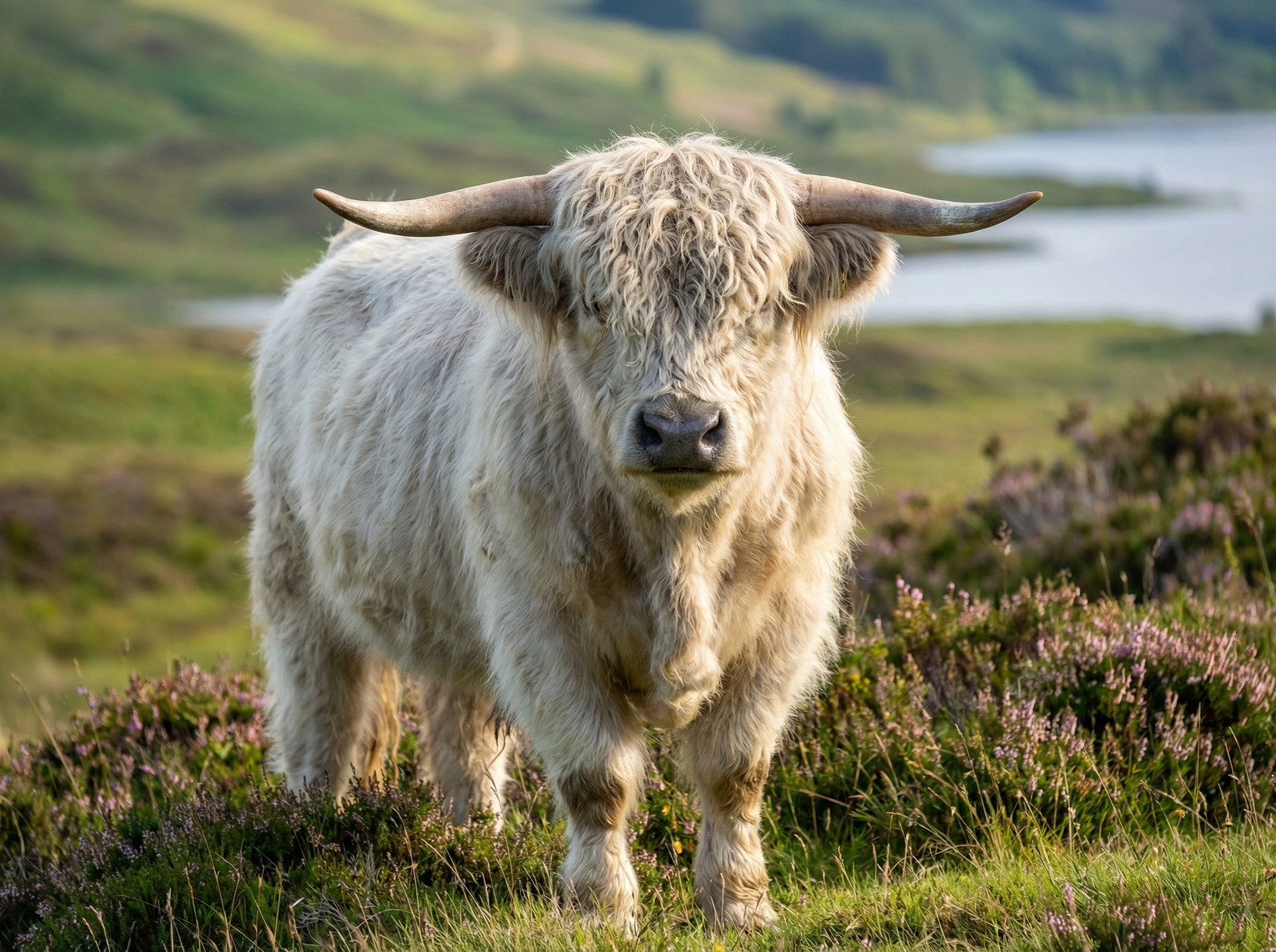 Highland Cattle
Highland Cattle
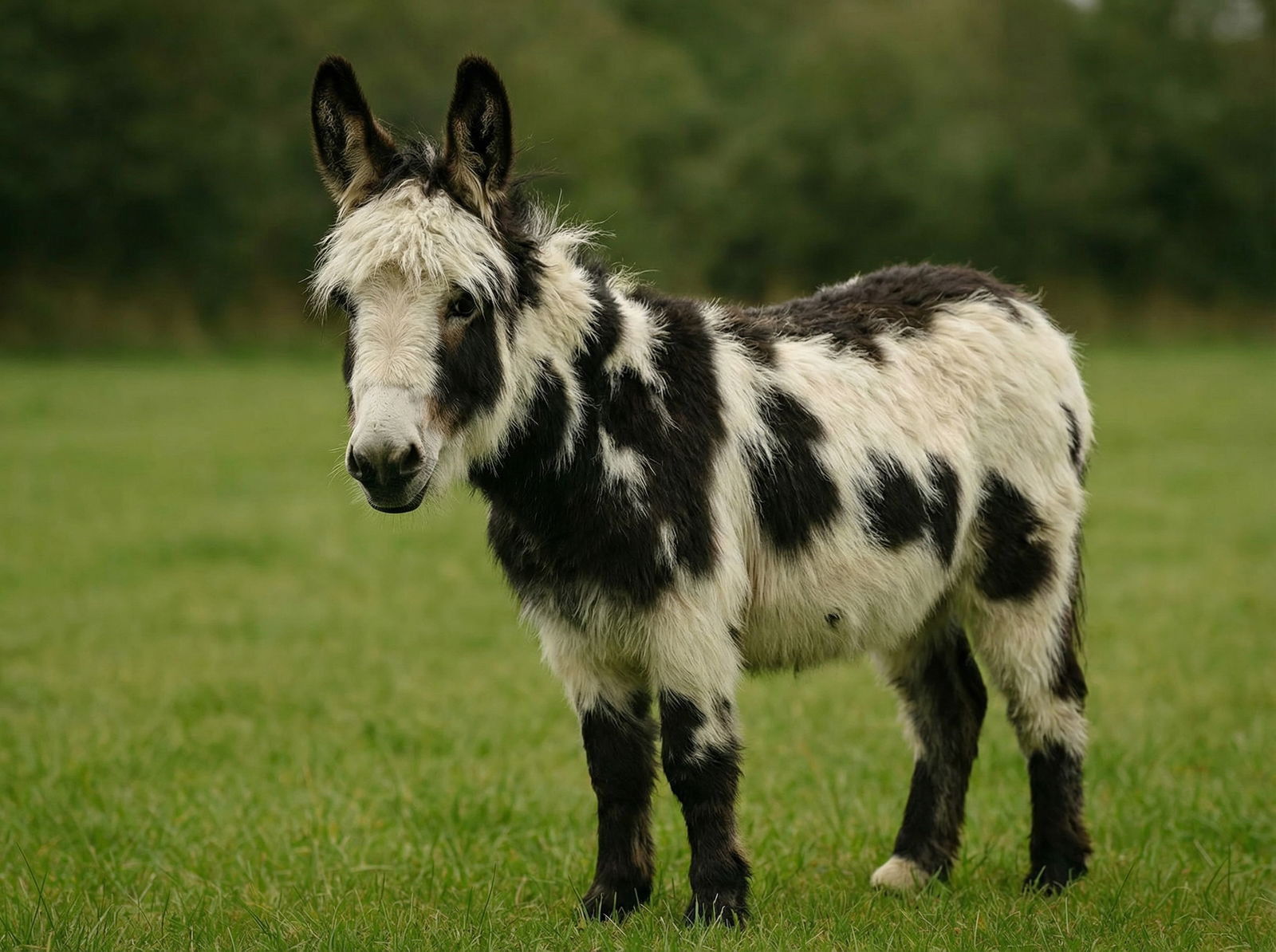 Miniature Donkeys
Miniature Donkeys
 All Species Directory
All Species Directory
 Highland Cattle in Virginia
Highland Cattle in Virginia
 Miniature Donkeys in Texas
Miniature Donkeys in Texas












